An inhibitory segment within G-patch activators tunes Prp43-ATPase activity during ribosome assembly
- PMID: 39578461
- PMCID: PMC11584650
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54584-5
An inhibitory segment within G-patch activators tunes Prp43-ATPase activity during ribosome assembly
Abstract
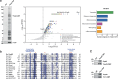
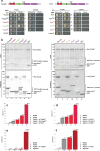
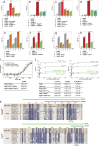
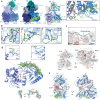
Mechanisms by which G-patch activators tune the processive multi-tasking ATP-dependent RNA helicase Prp43 (DHX15 in humans) to productively remodel diverse RNA:protein complexes remain elusive. Here, a comparative study between a herein and previously characterized activators, Tma23 and Pxr1, respectively, defines segments that organize Prp43 function during ribosome assembly. In addition to the activating G-patch, we discover an inhibitory segment within Tma23 and Pxr1, I-patch, that restrains Prp43 ATPase activity. Cryo-electron microscopy and hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry show how I-patch binds to the catalytic RecA-like domains to allosterically inhibit Prp43 ATPase activity. Tma23 and Pxr1 contain dimerization segments that organize Prp43 into higher-order complexes. We posit that Prp43 function at discrete locations on pre-ribosomal RNA is coordinated through toggling interactions with G-patch and I-patch segments. This could guarantee measured and timely Prp43 activation, enabling precise control over multiple RNA remodelling events occurring concurrently during ribosome formation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Bohnsack, K. E., Yi, S., Venus, S., Jankowsky, E. & Bohnsack, M. T. Cellular functions of eukaryotic RNA helicases and their links to human diseases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.24, 749–769 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Khreiss, A., Bohnsack, K. E. & Bohnsack, M. T. Molecular functions of RNA helicases during ribosomal subunit assembly. Biol. Chem.404, 781–789 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Ozgur, S. et al. The conformational plasticity of eukaryotic RNA-dependent ATPases. FEBS J.282, 850–863 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

