Lipid nanoparticle-mediated mRNA delivery to CD34+ cells in rhesus monkeys
- PMID: 39578569
- PMCID: PMC12095617
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-024-02470-2
Lipid nanoparticle-mediated mRNA delivery to CD34+ cells in rhesus monkeys
Abstract
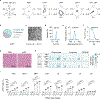
Transplantation of ex vivo engineered hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) can lead to robust clinical responses but carries risks of adverse events from bone marrow mobilization, chemotherapy conditioning and other factors. HSCs have been modified in vivo using lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) decorated with targeting moieties, which increases manufacturing complexity. Here we screen 105 LNPs without targeting ligands for effective homing to the bone marrow in mouse. We report an LNP named LNP67 that delivers mRNA to murine HSCs in vivo, primary human HSCs ex vivo and CD34+ cells in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) in vivo at doses of 0.25 and 0.4 mg kg-1. Without mobilization and conditioning, LNP67 can mediate delivery of mRNA to HSCs and their progenitor cells (HSPCs), as well as to the liver in rhesus monkeys, without serum cytokine activation. These data support the hypothesis that in vivo delivery to HSCs and HSPCs in nonhuman primates is feasible without targeting ligands.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: M.Z.C.H., H.N. and J.E.D. have filed a provisional patent related to this manuscript (US patent application number 63/632,354). J.E.D. is an advisor to GV, Readout, Edge Animal Health and Nava Therapeutics and P.J.S. is a cofounder of Tether Therapeutics. None of these companies provided any financial support for this work. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



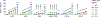
References
-
- Adams D et al. Patisiran, an RNAi therapeutic, for hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 379, 11–21 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Gillmore JD et al. CRISPR-Cas9 in vivo gene editing for transthyretin amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 385, 493–502 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Verve Therapeutics doses first human with an investigational in vivo base editing medicine, VERVE-101, as a potential treatment for heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. https://ir.vervetx.com/news-releases/news-release-details/verve-therapeu.... (2022).
Methods-only references
-
- Chen D et al. Rapid discovery of potent siRNA-containing lipid nanoparticles enabled by controlled microfluidic formulation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 6948–6951 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Mastronarde DN Automated electron microscope tomography using robust prediction of specimen movements. J. Struct. Biol. 152, 36–51 (2005). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UH3 TR002855/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P51 OD011107/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 DK136047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002378/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UH3-TR002855/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- U42 OD027094/CD/ODCDC CDC HHS/United States
- P51-OD011107/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- TL1DK136047/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- UG3 TR002855/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U42 OD027094/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

