Different dynamics of soluble inflammatory mediators after clearance of respiratory SARS-CoV-2 versus blood-borne hepatitis C virus infections
- PMID: 39578604
- PMCID: PMC11584618
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-79909-8
Different dynamics of soluble inflammatory mediators after clearance of respiratory SARS-CoV-2 versus blood-borne hepatitis C virus infections
Abstract
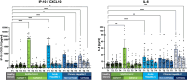
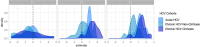
Viral infections can be acute or chronic, with the immune system pivotal in immunopathogenesis. The potential reversibility of inflammation post-viral elimination is of current interest. This study compares the dynamics of soluble inflammatory mediators (SIM) during and after respiratory infections with SARS-CoV-2 and blood-borne acute and chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections. The study included patients with acute HCV (n = 29), chronic HCV (n = 54), and SARS-CoV-2 (n = 39 longitudinal, n = 103 cross-sectional), along with 30 healthy controls. Blood samples were collected at baseline, end of treatment/infection, and during follow-up (up to 9 months). SIMs were quantified using the HD-SP-X Imaging and Analysis System™. At baseline, SIM profiles in acute SARS-CoV-2 and HCV infections were significantly elevated compared with controls. During follow-up, SIM decline was less pronounced in acute and chronic HCV infections after successful therapy than in SARS-CoV-2 infections. Most SIM in the SARS-CoV-2 cohort normalized within 3 months. In chronic HCV, SIM were higher in cirrhotic than noncirrhotic patients post-HCV elimination. Dynamics of SIM after viral elimination vary between blood-borne acute and chronic HCV infections and respiratory SARS-CoV-2 infections. Immunological imprints 3-9 months after HCV elimination appear more pronounced than after SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chemokines; Cirrhosis; Cytokines; Direct-acting antiviral; Hepatitis C virus; Immune mediators; Inflammation; Long-COVID; Proteomics; SARS-CoV-2 infection; Sustained virological response.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Narasimhan, H., Wu, Y., Goplen, N. P. & Sun, J. Immune determinants of chronic sequelae after respiratory viral infection. Sci. Immunol.7, eabm7996 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Altmann, D. M., Whettlock, E. M., Liu, S., Arachchillage, D. J. & Boyton, R. J. The immunology of long COVID. Nat. Rev. Immunol.10.1038/s41577-023-00904-7 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

