Attention-based multi-residual network for lung segmentation in diseased lungs with custom data augmentation
- PMID: 39578613
- PMCID: PMC11584877
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-79494-w
Attention-based multi-residual network for lung segmentation in diseased lungs with custom data augmentation
Abstract
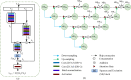
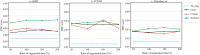
Lung disease analysis in chest X-rays (CXR) using deep learning presents significant challenges due to the wide variation in lung appearance caused by disease progression and differing X-ray settings. While deep learning models have shown remarkable success in segmenting lungs from CXR images with normal or mildly abnormal findings, their performance declines when faced with complex structures, such as pulmonary opacifications. In this study, we propose AMRU++, an attention-based multi-residual UNet++ network designed for robust and accurate lung segmentation in CXR images with both normal and severe abnormalities. The model incorporates attention modules to capture relevant spatial information and multi-residual blocks to extract rich contextual and discriminative features of lung regions. To further enhance segmentation performance, we introduce a data augmentation technique that simulates the features and characteristics of CXR pathologies, addressing the issue of limited annotated data. Extensive experiments on public and private datasets comprising 350 cases of pneumoconiosis, COVID-19, and tuberculosis validate the effectiveness of our proposed framework and data augmentation technique.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
AMFP-net: Adaptive multi-scale feature pyramid network for diagnosis of pneumoconiosis from chest X-ray images.Artif Intell Med. 2024 Aug;154:102917. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2024.102917. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Artif Intell Med. 2024. PMID: 38917599
-
CAD-Unet: A capsule network-enhanced Unet architecture for accurate segmentation of COVID-19 lung infections from CT images.Med Image Anal. 2025 Jul;103:103583. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2025.103583. Epub 2025 Apr 19. Med Image Anal. 2025. PMID: 40306203
-
DDA-SSNets: Dual decoder attention-based semantic segmentation networks for COVID-19 infection segmentation and classification using chest X-Ray images.J Xray Sci Technol. 2024;32(3):623-649. doi: 10.3233/XST-230421. J Xray Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 38607728
-
A review on lung boundary detection in chest X-rays.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2019 Apr;14(4):563-576. doi: 10.1007/s11548-019-01917-1. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2019. PMID: 30730032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Segmentation and Image Analysis of Abnormal Lungs at CT: Current Approaches, Challenges, and Future Trends.Radiographics. 2015 Jul-Aug;35(4):1056-76. doi: 10.1148/rg.2015140232. Radiographics. 2015. PMID: 26172351 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lung image segmentation with improved U-Net, V-Net and Seg-Net techniques.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2025 Feb 13;11:e2700. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2700. eCollection 2025. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2025. PMID: 40062241 Free PMC article.
-
Lung Segmentation with Lightweight Convolutional Attention Residual U-Net.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Mar 27;15(7):854. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15070854. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218203 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

