Spatial and single-nucleus transcriptomic analysis of genetic and sporadic forms of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 39578645
- PMCID: PMC11631771
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01961-x
Spatial and single-nucleus transcriptomic analysis of genetic and sporadic forms of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
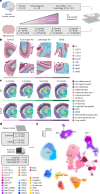
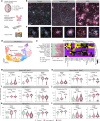
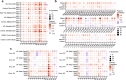
The pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) depends on environmental and heritable factors, with its molecular etiology still unclear. Here we present a spatial transcriptomic (ST) and single-nucleus transcriptomic survey of late-onset sporadic AD and AD in Down syndrome (DSAD). Studying DSAD provides an opportunity to enhance our understanding of the AD transcriptome, potentially bridging the gap between genetic mouse models and sporadic AD. We identified transcriptomic changes that may underlie cortical layer-preferential pathology accumulation. Spatial co-expression network analyses revealed transient and regionally restricted disease processes, including a glial inflammatory program dysregulated in upper cortical layers and implicated in AD genetic risk and amyloid-associated processes. Cell-cell communication analysis further contextualized this gene program in dysregulated signaling networks. Finally, we generated ST data from an amyloid AD mouse model to identify cross-species amyloid-proximal transcriptomic changes with conformational context.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures














Update of
-
Spatial and single-nucleus transcriptomic analysis of genetic and sporadic forms of Alzheimer's Disease.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 26:2023.07.24.550282. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.24.550282. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Genet. 2024 Dec;56(12):2704-2717. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-01961-x. PMID: 37546983 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30 AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AG054349/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG071683/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD087011/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD105353/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG051412/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002373/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062715/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AG076308/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS135556/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001857/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066519/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG068054/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA053826/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG000096/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001414/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS084974/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD090256/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG071683/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG051406/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001873/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

