Interaction Between DHCR24 and hsa_circ_0015335 Facilitates Cognitive Impairment in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Patients
- PMID: 39578712
- PMCID: PMC11584349
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.70131
Interaction Between DHCR24 and hsa_circ_0015335 Facilitates Cognitive Impairment in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Patients
Abstract
Aims: The study attempted to determine the underlying role and regulation mechanism of 3β-hydroxysterol-Δ24 reductase (DHCR24) in the pathophysiology of cerebral small vessel disease-associated cognitive impairment (CSVD-CI). An RNA high-throughput sequencing and independent verification were conducted to identify potential circRNAs becoming the upstream regulator.
Methods: RNA sequencing was performed in whole-blood samples in cohort 1 (10 CSVD-CI and 8 CSVD with cognitively normal [CSVD-CN] patients). The DHCR24 and candidate circRNAs were verified in an independent cohort 2 (45 CSVD-CI participants and 37 CSVD-CN ones). The study also analyzed comprehensive cognitive assessments, plasma molecular index, and brain structure imaging.
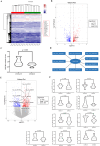
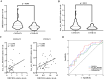
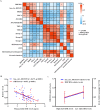
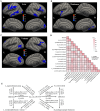
Results: The expression of DHCR24 and has_circ_0015335 in whole-blood samples of CSVD-CI patients was significantly reduced compared to CSVD-CN patients in RNA sequencing and independent verification. Furthermore, the levels of DHCR24 and has_circ_0015335 were significantly related to global cognitive impairment in CSVD-CI patients. Meanwhile, DHCR24 could regulate the correlation between has_circ_0015335 expression and alterations in brain cortex in surface area, thickness, and volume in CSVD-CI patients. Additionally, hsa_circ_0015335 interacted with DHCR24 for plasma 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol levels among CSVD-CI patients.
Conclusion: Interaction between DHCR24 and hsa_circ_0015335 cognitively impaired CSVD by affecting brain cholesterol metabolism and brain structural changes.
Keywords: brain magnetic resonance imaging; cerebral small vessel disease; cholesterol metabolism; circRNA; cognitive impairment; mRNA.
© 2024 The Author(s). CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wang J., Zhang Y., Tian N., et al., “Mechanisms of Glutamate Metabolic Function and Dysfunction in Vascular Dementia,” Neuroprotection 2 (2024): 33–48, 10.1002/nep3.32. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- JSSCBS20221995/Jiangsu province double-creation doctoral talent plan
- 2021THRC-TF-YXYXK/the Medical Expert Team Program of Wuxi Taihu Talent Plan 2021
- Q202222/the WuXi Municipal Health Commission
- 82301715/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020THRC-DJ-SNW/Wuxi Taihu Lake Talent Plan, Supports for Leading Talents in Medical and Health Profession
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

