Effectiveness of geriatric rehabilitation in inpatient and day hospital settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39578865
- PMCID: PMC11583748
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-024-03764-7
Effectiveness of geriatric rehabilitation in inpatient and day hospital settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Geriatric rehabilitation is a multidisciplinary intervention that promotes functional recovery in older adults. Our objective was to assess the efficacy of geriatric rehabilitation in inpatient and geriatric day hospital settings.
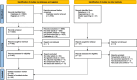
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, PsycINFO, PEDro and AgeLine from inception to September 30, 2022 for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) including older adults (age ≥ 65 years) undergoing geriatric rehabilitation (inpatient or day hospital) with a usual care comparator group. Primary outcome measures included mortality, long-term care home (LTCH) admission, and functional status. Secondary outcomes included discharge/remaining at home, functional improvement, length of stay, cognition, mood, and quality of life. Records were screened, abstracted and assessed for risk of bias (Cochrane Risk of Bias [RoB] 2) by two reviewers independently. We conducted a random effects meta-analysis to summarize risk ratios (RR, dichotomous outcomes) and standardized mean differences (SMD, continuous outcomes).
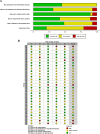
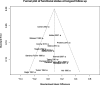
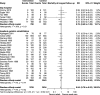
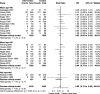
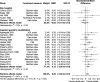
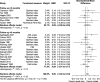
Results: Of the 5304 records screened, 29 studies (7999 patients) met eligibility criteria. There were 23 RCTs of inpatient geriatric rehabilitation (6428 patients) and six of geriatric day hospital (1571 patients) reporting outcomes of mortality (26 studies), LTCH admission (22 studies), functional status (19 studies), length of stay (18 studies), cognition (5 studies), mood (5 studies) and quality of life (6 studies). The primary outcome of mortality at longest follow up was lower in the rehabilitation group (RR 0.84, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.76 to 0.93, I2 = 0%). LTCH admission was lower in the rehabilitation group at longest follow up (RR 0.86, 95% CI 0.75 to 0.98, I2 = 8%). Functional status was better in the rehabilitation group at longest follow up (SMD 0.09, 95% CI 0.02 to 0.16, I2 = 24%). Cognition was improved in the rehabilitation group (mean difference of mini-mental status exam score 0.97, 95% CI 0.35 to 1.60, I2 = 0%). No difference was found for patient length of stay, mood, or quality of life.
Conclusions: Geriatric rehabilitation in inpatient and day hospital settings reduced mortality, LTCH admission, and functional impairment. Future studies should explore implementation of this intervention for older adults.
Review registration: PROSPERO: CRD42022345078.
Keywords: Cognition; Day hospital; Functional status; Geriatric rehabilitation; Inpatient; Long-term care; Mortality; Older adults.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization. Rehabilitation in Health Systems. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241549974.
-
- World Health Organization. Rehabilitation 2030. WHO. 2021. https://www.who.int/initiatives/rehabilitation-2030. Accessed 28 Mar 2022.
-
- van Balen R, Gordon AL, Schols JMGA, Drewes YM, Achterberg WP. What is geriatric rehabilitation and how should it be organized? A Delphi study aimed at reaching European consensus. Eur Geriatr Med. 2019;10:977–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

