Multi-site Ultrasound-guided Fine Needle Aspiration to Study Cells and Soluble Factors From Human Lymph Nodes
- PMID: 39579041
- PMCID: PMC11585077
- DOI: 10.1002/cpz1.70063
Multi-site Ultrasound-guided Fine Needle Aspiration to Study Cells and Soluble Factors From Human Lymph Nodes
Abstract
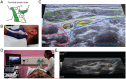
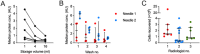
Lymph nodes (LNs) are specialized secondary lymphoid tissues essential to the priming and maintenance of adaptive immune responses, including the B cell germinal center response; thus, they are central to immunity. However, the anatomically restricted and time-resolved nature of immune priming means that sampling disease-relevant human LNs requires specialized techniques. This article describes the application of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (FNA) to sample LNs, using cervical LNs of the head and neck as an exemplar. This minimally invasive technique allows collection of both immune cells and cell-free material that are relevant to both neuroimmune diseases and basic lymphatic functions. Downstream use of cellular material can include multiplexed flow cytometry, single-cell transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq), and B cell cultures. The cell-free supernatant can be used for proteomics or other similar 'omics approaches. This unit describes collection of samples by FNA as well as processing and storage of samples for downstream assays. © 2024 The Author(s). Current Protocols published by Wiley Periodicals LLC. Basic Protocol 1: Sampling of human cervical lymph nodes by ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration Alternate Protocol: Sampling of human lymph nodes by ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration with negative pressure Basic Protocol 2: Processing and storage of human lymph node samples.
Keywords: cervical lymph nodes; fine needle aspiration; lymph; lymph node.
© 2024 The Author(s). Current Protocols published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
N.M.P. has received consulting fees from Infinitopes, LLC. K.M.P. has received payment or honoraria from CSL Seqirus and Sanofi Pasteur, and has participated in data safety monitoring boards for Moderna.
Figures


References
-
- Al‐Diwani, A. , Provine, N. M. , Murchison, A. , Laban, R. , Swann, O. J. , Koychev, I. , Sheerin, F. , Mesquita, S. D. , Heslegrave, A. , Zetterberg, H. , Klenerman, P. , & Irani, S. R. (2024). Neurodegenerative fluid biomarkers are enriched in human cervical lymph nodes. Brain, awae329. 10.1093/brain/awae329 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al‐Diwani, A. , Theorell, J. , Damato, V. , Bull, J. , McGlashan, N. , Green, E. , Kienzler, A. K. , Harrison, R. , Hassanali, T. , Campo, L. , Browne, M. , Easton, A. , Soleymani Majd, H. , Tenaka, K. , Iorio, R. , Dale, R. C. , Harrison, P. , Geddes, J. , Quested, D. , … Irani, S. R. (2022). Cervical lymph nodes and ovarian teratomas as germinal centres in NMDA receptor‐antibody encephalitis. Brain, 145, 2742–2754. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Broggi, M. A. S. , Maillat, L. , Clement, C. C. , Bordry, N. , Corthésy, P. , Auger, A. , Matter, M. , Hamelin, R. , Potin, L. , Demurtas, D. , Romano, E. , Harari, A. , Speiser, D. E. , Santambrogio, L. , & Swartz, M. A. (2019). Tumor‐associated factors are enriched in lymphatic exudate compared to plasma in metastatic melanoma patients. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 216, 1091–1107. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clement, C. C. , Aphkhazava, D. , Nieves, E. , Callaway, M. , Olszewski, W. , Rotzschke, O. , & Santambrogio, L. (2013). Protein expression profiles of human lymph and plasma mapped by 2D‐DIGE and 1D SDS–PAGE coupled with nanoLC–ESI–MS/MS bottom‐up proteomics. Journal of Proteomics, 78, 172–187. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

