Development of Zinc-Containing Chitosan/Gelatin Coatings with Immunomodulatory Effect for Soft Tissue Sealing around Dental Implants
- PMID: 39579168
- PMCID: PMC11711843
- DOI: 10.1007/s13770-024-00680-y
Development of Zinc-Containing Chitosan/Gelatin Coatings with Immunomodulatory Effect for Soft Tissue Sealing around Dental Implants
Abstract
Background: Soft tissue integration (STI) around dental implant abutments is a prerequisite to prevent bacterial invasion and achieve successful dental implant rehabilitation. However, peri-implant STI is a major challenge after dental abutment placement due to alterations in the immune microenvironment upon surgical dental implant installation.
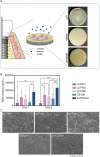
Methods: Based on known immunomodulatory effects of zinc, we herein deposited zinc/chitosan/gelatin (Zn/CS/Gel) coatings onto titanium substrates to study their effect on macrophages. First, we exposed macrophages to cell culture media containing different zinc ion (Zn2+) concentrations. Next, we explored the immunomodulatory effect of Zn/CS/Gel coatings prepared via facile electrophoretic deposition (EPD).
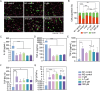
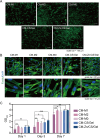
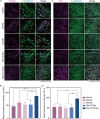
Results: We found that Zn2+ effectively altered the secretome by reducing the secretion of pro-inflammatory and enhancing pro-regenerative cytokine secretion, particularly at a Zn2+ supplementation of approximately 37.5 μM. Zn/CS/Gel coatings released Zn2+ in a concentration range which effectively stimulated pro-regenerative macrophage polarization as demonstrated by M2 macrophage polarization. Additionally, the impact of these Zn2+-exposed macrophages on gingival fibroblasts incubated in conditioned medium showed stimulated adhesion, proliferation, and collagen secretion.
Conclusion: Our promising results suggest that controlled release of Zn2+ from Zn/CS/Gel coatings could be applied to immunomodulate peri-implant STI, and to enhance dental implant survival.
Keywords: Chitosan; Gelatin; Macrophage; Soft tissue integration; Zinc ion.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical Approval: There are no animal experiments carried out for this article.
Figures



References
-
- Mauland EK, Bull VH, Melbye EL, Verket A. Patient-reported outcomes following dental implant rehabilitation according to reason for missing teeth: a survey from a Norwegian population 8 years following treatment. J Clin Periodontol. 2024;51:135–144. - PubMed
-
- Franz S, Rammelt S, Scharnweber D, Simon JC. Immune responses to implants-a review of the implications for the design of immunomodulatory biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2011;32:6692–709. - PubMed
-
- Liu RH, Chen SC, Huang PN, Liu GQ, Luo P, Li ZP, et al. Immunomodulation-based strategy for improving soft tissue and metal implant integration and its implications in the development of metal soft tissue materials. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30:1910672.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
