Immunoexpression of placental growth factor (PlGF) and soluble FMS-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFlt-1) in the placental bed of preeclamptic women of African ancestry living with HIV infection
- PMID: 39579213
- PMCID: PMC11585514
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-024-02341-6
Immunoexpression of placental growth factor (PlGF) and soluble FMS-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFlt-1) in the placental bed of preeclamptic women of African ancestry living with HIV infection
Abstract
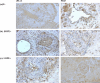
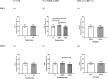
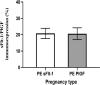
Preeclampsia, a severe pregnancy complication linked to defective placentation, poses significant maternal risks and is characterized by dysregulated angiogenic factors, including placental growth factor (PlGF) and soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1). Women with HIV/AIDS and receiving ART may face an increased susceptibility to preeclampsia development due to immunological and angiogenic imbalance. This study investigates the immunoexpression of these factors in the context of HIV-associated preeclampsia, utilizing morphometric image analysis. The study cohort comprised 180 women, including 60 normotensive and 120 preeclamptic participants, further stratified by HIV status and gestational age (early-onset PE [EOPE] < 34 weeks and late-onset PE [LOPE] ≥ 34 weeks). Placental bed tissues were immunostained with mouse anti-human sFlt-1 and PlGF antibodies, and the results were analyzed using Zeiss Axio-Vision and GraphPad Prism software. sFlt-1 levels showed no significant overall difference between preeclamptic and normotensive women (p = 0.8661), though slightly increased in the preeclamptic myometrium, independent of HIV status. However, sFlt-1 levels were significantly higher in EOPE compared to both normotensive and LOPE groups. PlGF immunostaining also showed no significant overall difference (p = 0.7387) but was notably lower in preeclamptic pregnancies and significantly higher in EOPE compared to LOPE. HIV status did not significantly impact sFlt-1 or PlGF levels, although sFlt-1 was slightly higher in HIV-negative women, while PlGF was marginally higher in HIV-positive women. These findings highlight the complex role of angiogenic factors in preeclampsia pathophysiology and suggest that antiretroviral therapies (ARTs) may contribute to the dysregulation of these factors due to a heightened immune milieu.
Keywords: HIV; Immunohistochemistry; PlGF; Preeclampsia; sFlt-1.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Akinsanya OS, Wiseberg-Firtell J, Akpomiemie G et al (2017) Evaluation of the prevention of mother-to-child transmission programme at a primary health care centre in South Africa. SAFP 59:56–60
-
- Bulmer JN, Williams PJ, Lash GE (2010) Immune cells in the placental bed. Int J Dev Biol 54:281–294 - PubMed
-
- Carrasco-Wong I, Aguilera-Olguín M, Escalona-Rivano R et al (2021) Syncytiotrophoblast stress in early onset preeclampsia: The issues perpetuating the syndrome. Placenta 113:57–66 - PubMed
-
- Cele S, Odun-Ayo F, Onyangunga O et al (2018) Analysis of hepatocyte growth factor immunostaining in the placenta of HIV-infected normotensive versus preeclamptic pregnant women. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 227:60–66 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

