Exploring new mechanisms in cancer molecular pathways and pathogenic cell transformation: PIP4K2A as a prognostic marker and therapeutic target in cutaneous malignant melanoma
- PMID: 39579298
- PMCID: PMC11585527
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01555-3
Exploring new mechanisms in cancer molecular pathways and pathogenic cell transformation: PIP4K2A as a prognostic marker and therapeutic target in cutaneous malignant melanoma
Abstract
Background: Cutaneous malignant melanoma is a very aggressive and metastatic form of skin cancer, typically linked with poor outcomes. Advances in genomic analysis have underscored the crucial role of T cells in tumor immunity. Immune checkpoint inhibitors have notably transformed melanoma treatment by boosting T cell activity. Studies of gene expression have found that the phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate kinase 2A (PIP4K2A) gene is abnormally expressed in various tumors, indicating its potential role in tumor progression. Utilizing single-cell sequencing and machine learning, researchers can now explore the complex interactions between T cells and melanoma cells at a genomic level. This study aimed to investigate the role of the PIP4K2A gene in cutaneous malignant melanoma, with a focus on its influence on T cell-mediated immune responses.
Methods: Samples from cutaneous melanoma patients were analysed by single-cell transcriptome for differentially expressed genes and signalling pathways associated with cutaneous melanoma. Then, genes were identified and predictive models were built based on the transcriptomic data using machine learning models to assess whether the expression level of PIP4K2A could effectively predict the malignancy and prognosis of cutaneous melanoma. In addition, we also performed drug therapy predictive analysis and immunotherapy analysis.Finally, the critical role of PIP4K2A in cutaneous melanoma was further confirmed by immunohistochemistry.
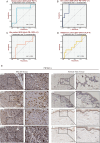
Results: The PIP4K2A gene exhibited a significantly elevated expression level in cutaneous malignant melanoma, showing a strong correlation with the clinical stage and patient prognosis. At the therapeutic level, high PIP4K2A expression is less responsive to immunotherapy, and this gene is a risk factor for drug therapy in cutaneous malignant melanoma. Additionally, our experimental outcomes validated this observation.
Conclusions: The PIP4K2A gene could be a crucial prognostic marker for cutaneous malignant melanoma, as it significantly affects T cell activity within the tumor microenvironment. This study offers essential insights into melanoma pathogenesis and assists in pinpointing new early diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets. Utilizing advanced genomic tools and computational techniques, the research enhances our understanding of T cell dynamics in melanoma, facilitating the development of personalized medicine and more effective immunotherapy strategies.
Keywords: Machine learning; PIP4K2A; ScRNA-seq; Single-cell transcriptome; Skin cutaneous melanoma (SKCM); T cell.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study involving human participants was conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee, as well as the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The research protocol was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Jinzhou Medical University. Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Consent for publication: Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study. In cases where participants were under 18 years of age, consent was obtained from a parent or legal guardian. Consent to participate and consent to publish the results was also obtained from all participants or their legal representatives, ensuring adherence to ethical guidelines. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Walker GJ, Hayward NK. Pathways to melanoma development: lessons from the mouse. J Invest Dermatol. 2002;119:783–92. 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2002.00217.x. - PubMed
-
- Feng D, Liu S, Li D, Han P, Wei W. Analysis of conventional versus advanced pelvic floor muscle training in the management of urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Transl Androl Urol. 2020;9(5):2031–45. 10.21037/tau-20-615. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnold M, de Vries E, Whiteman DC, Jemal A, Bray F, Parkin DM, Soerjomataram I. Global burden of cutaneous melanoma attributable to ultraviolet radiation in 2012. Int J Cancer. 2018;143:1305–14. 10.1002/ijc.31527. - PubMed
-
- Hawkes JE, Truong A, Meyer LJ. Genetic predisposition to melanoma. Semin Oncol. 2016;43:591–7. 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2016.08.003. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
