Multielectrode catheter-based pulsed electric field vs. cryoballoon for atrial fibrillation ablation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39579376
- PMCID: PMC11641428
- DOI: 10.1093/europace/euae293
Multielectrode catheter-based pulsed electric field vs. cryoballoon for atrial fibrillation ablation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Aims: Pulsed field ablation (PFA) is an innovative technology recently adopted for the treatment of atrial fibrillation (AF). Preclinical and clinical studies have reported a remarkable safety profile, as a result of its tissue-specific effect targeting cardiomyocytes and sparing adjacent tissues. Single-shot pentaspline system was the first PFA device to receive regulatory approval. We performed a meta-analysis to compare the efficacy and safety of PFA with the single-shot pentaspline system vs. currently available second-/third-/fourth-generation cryoballoon ablation (CRYO) technologies.
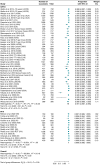
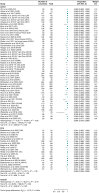
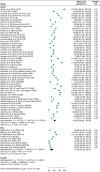
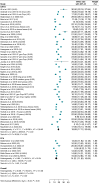
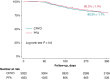
Methods and results: We systematically searched electronic databases for studies focusing on AF ablation employing the PFA single-shot pentaspline system or second-/third-/fourth-generation CRYO technologies. The primary endpoints were acute procedural success assessed on a vein and patient basis. Safety endpoints included overall periprocedural complications and major periprocedural complications. We also compared procedural, fluoroscopy times, and freedom from atrial tachyarrhythmias (ATs) at follow-up (secondary endpoints). Twenty and 70 studies were included for PFA and CRYO, respectively. Pulsed field ablation demonstrated greater acute procedural success on a vein basis (99.9% vs. 99.1%; P < 0.001), as well as per patient (99.5% vs. 98.4%; P < 0.001). Pulsed field ablation yielded lower overall periprocedural complications (3.1% vs. 5.6%; P < 0.001), shorter procedural time (75.9 min vs. 105.6 min; P < 0.001), and fluoroscopy time (14.2 min vs. 18.9 min; P < 0.001) compared with CRYO. No differences were found for major periprocedural complications (1.2% vs. 1.0%; P = 0.46) and freedom from ATs at 1 year (82.3% vs. 80.3%; log-rank P = 0.61).
Conclusion: Pulsed field ablation contributed to higher acute procedural success and safety compared with CRYO. No statistically significant differences in AT recurrence at 1-year follow-up were observed.
Keywords: Ablation; Atrial fibrillation; Catheter ablation; Cryoballoon ablation; Pulmonary vein isolation; Pulsed field ablation.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests. A.N. received speaker honoraria from Boston Scientific, Biosense Webster, Abbott, Biotronik, and Medtronic and is a consultant for Biosense Webster, Abbott, and Janssen. G.-B.C. received compensation for teaching purposes and proctoring from Medtronic, Abbott, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and Acutus Medical. C.d.A. receives research grants on behalf of the centre from Biotronik, Medtronic, Abbott, LivaNova, Boston Scientific, AtriCure, Philips, and Acutus. The other authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist C et al. 2020 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur Heart J 2021;42:373–498. - PubMed
-
- Andrade JG, Wells GA, Deyell MW, Bennett M, Essebag V, Champagne J et al. Cryoablation or drug therapy for initial treatment of atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2021;384:305–15. - PubMed
-
- Kirchhof P, Camm AJ, Goette A, Brandes A, Eckardt L, Elvan A et al. Early rhythm-control therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2020;383:1305–16. - PubMed
-
- Kuck K-H, Brugada J, Fürnkranz A, Metzner A, Ouyang F, Chun KRJ et al. Cryoballoon or radiofrequency ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2016;374:2235–45. - PubMed
-
- Del Monte A, Chierchia GB, Della Rocca DG, Pannone L, Sorgente A, Bala G et al. Posterior wall isolation via a multi-electrode radiofrequency balloon catheter: feasibility, technical considerations, endoscopic findings and comparison with cryoballoon technologies. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 2023;67:273–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

