The cell adhesion molecule CD44 acts as a modulator of 5-HT7 receptor functions
- PMID: 39580460
- PMCID: PMC11585102
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-024-01931-0
The cell adhesion molecule CD44 acts as a modulator of 5-HT7 receptor functions
Abstract
Background: Homo- and heteromerization of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) plays an important role in the regulation of receptor functions. Recently, we demonstrated an interaction between the serotonin receptor 7 (5-HT7R), a class A GPCR, and the cell adhesion molecule CD44. However, the functional consequences of this interaction on 5-HT7R-mediated signaling remained enigmatic.
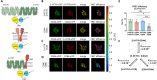
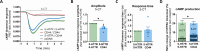
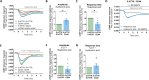
Methods: Using a quantitative FRET (Förster resonance energy transfer) approach, we determined the affinities for the formation of homo- and heteromeric complexes of 5-HT7R and CD44. The impact of heteromerization on 5-HT7R-mediated cAMP signaling was assessed using a cAMP responsive luciferase assay and a FRET-based cAMP biosensor under basal conditions as well as upon pharmacological modulation of the 5-HT7R and/or CD44 with specific ligands. We also investigated receptor-mediated G protein activation using BRET (bioluminescence resonance energy transfer)-based biosensors in both, homo- and heteromeric conditions. Finally, we analyzed expression profiles for 5-HT7R and CD44 in the brain during development.
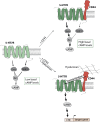
Results: We found that homo- and heteromerization of the 5-HT7R and CD44 occur at similar extent. Functionally, heteromerization increased 5-HT7R-mediated cAMP production under basal conditions. In contrast, agonist-mediated cAMP production was decreased in the presence of CD44. Mechanistically, this might be explained by increased Gαs and decreased GαoB activation by 5-HT7R/CD44 heteromers. Unexpectedly, treatment of the heteromeric complex with the CD44 ligand hyaluronic acid boosted constitutive 5-HT7R-mediated cAMP signaling and receptor-mediated transcription, suggesting the existence of a transactivation mechanism.
Conclusions: Interaction with the hyaluronan receptor CD44 modulates both the constitutive activity of 5-HT7R as well as its agonist-mediated signaling. Heteromerization also results in the transactivation of 5-HT7R-mediated signaling via CD44 ligand.
Keywords: Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET); Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET); G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR); Hyaluronan receptor CD44; Receptor oligomerization; Serotonin receptor 7 (5-HT7R).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Rios CD, Jordan BA, Gomes I, Devi LA. G-protein-coupled receptor dimerization: modulation of receptor function. Pharmacol Ther. 2001;92(2):71–87. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

