A multi-region single nucleus transcriptomic atlas of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 39580497
- PMCID: PMC11585549
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-024-04117-y
A multi-region single nucleus transcriptomic atlas of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Parkinson's Disease (PD) is a debilitating neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by motor and cognitive impairments, that affects >1% of the population over the age of 60. The pathogenesis of PD is complex and remains largely unknown. Due to the cellular heterogeneity of the human brain and changes in cell type composition with disease progression, this complexity cannot be fully captured with bulk tissue studies. To address this, we generated single-nucleus RNA sequencing and whole-genome sequencing data from 100 postmortem cases and controls, carefully selected to represent the entire spectrum of PD neuropathological severity and diverse clinical symptoms. The single nucleus data were generated from five brain regions, capturing the subcortical and cortical spread of PD pathology. Rigorous preprocessing and quality control were applied to ensure data reliability. Committed to collaborative research and open science, this dataset is available on the AMP PD Knowledge Platform, offering researchers a valuable tool to explore the molecular bases of PD and accelerate advances in understanding and treating the disease.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Panos Roussos is an Editorial Board Member for Scientific Data.
Figures

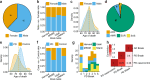


References
-
- Goedert, M., Spillantini, M. G., Del Tredici, K. & Braak, H. 100 years of Lewy pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurol.9, 13–24 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Shahmoradian, S. H. et al. Lewy pathology in Parkinson’s disease consists of crowded organelles and lipid membranes. Nat. Neurosci.22, 1099–1109 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Ascherio, A. & Schwarzschild, M. A. The epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease: risk factors and prevention. Lancet Neurol.15, 1257–1272 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

