Epidemiology of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: a multicenter, prospective, observational cohort study in South Korea
- PMID: 39581988
- PMCID: PMC11587587
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-024-05167-9
Epidemiology of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: a multicenter, prospective, observational cohort study in South Korea
Abstract
Background: Despite the clinical importance of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury (SA-AKI), little is known about its epidemiology. We aimed to investigate the incidence and outcomes of SA-AKI, as well as the risk factors for mortality among patients with severe SA-AKI in critically ill patients.
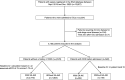
Methods: This secondary multicenter, observational, prospective cohort analysis of sepsis in South Korea evaluated patients aged ≥ 19 years admitted to intensive care units with a diagnosis of sepsis. The primary outcome was the incidence of SA-AKI, defined using the new consensus definition of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative 28 Workgroup. Secondary outcomes were in-hospital mortality and risk factors for in-hospital mortality.
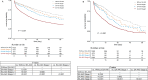
Results: Between September 2019 and December 2022, 5100 patients were admitted to intensive care units with a diagnosis of sepsis, and 3177 (62.3%) developed SA-AKI. A total of 613 (19.3%), 721 (22.7%), and 1843 (58.0%) patients had stage 1, 2, and 3 SA-AKI, respectively. Severe SA-AKI (stages 2 and 3 combined) was associated with an increased risk of in-hospital mortality. Adherence to the fluid resuscitation component of the one-hour sepsis bundle was associated with a decreased risk of in-hospital mortality in severe SA-AKI (adjusted odds ratio, 0.62; 95% confidence interval, 0.48-0.79; P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Of the patients admitted to the intensive care unit for sepsis, 62.3% developed SA-AKI. Severe SA-AKI was associated with an increased risk of mortality. Adherence to the fluid resuscitation component of the one-hour sepsis bundle can potentially improve outcomes in these patients.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Epidemiology; Intensive care unit; Kidney; Sepsis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Availability of data and materials: No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study. The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the institutional review boards of each participating hospital, including the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital (IRB number: B-1810-500-402). The requirement for informed consent was waived because of the noninterventional, observational nature of the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM, Hotchkiss RS, Levy MM, Marshall JC, Martin GS, Opal SM, Rubenfeld GD, van der Poll T, Vincent JL, Angus DC. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016;315:801–10. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, Colombara DV, Ikuta KS, Kissoon N, Finfer S, Fleischmann-Struzek C, Machado FR, Reinhart KK, Rowan K, Seymour CW, Watson RS, West TE, Marinho F, Hay SI, Lozano R, Lopez AD, Angus DC, Murray CJL, Naghavi M. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: analysis for the global burden of disease study. Lancet. 2020;395:200–11. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, Bouman C, Macedo E, Gibney N, Tolwani A, Ronco C. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA. 2005;294:813–8. - PubMed
-
- Hoste EA, Bagshaw SM, Bellomo R, Cely CM, Colman R, Cruz DN, Edipidis K, Forni LG, Gomersall CD, Govil D, Honoré PM, Joannes-Boyau O, Joannidis M, Korhonen AM, Lavrentieva A, Mehta RL, Palevsky P, Roessler E, Ronco C, Uchino S, Vazquez JA, Vidal Andrade E, Webb S, Kellum JA. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: the multinational AKI-EPI study. Intensive Care Med. 2015;41:1411–23. - PubMed

