Tropism of adeno-associated virus serotypes in mouse lungs via intratracheal instillation
- PMID: 39581991
- PMCID: PMC11587702
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-024-02575-9
Tropism of adeno-associated virus serotypes in mouse lungs via intratracheal instillation
Abstract
Background: Gene therapy holds great potential for treating various acquired and inherited pulmonary diseases. Adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors have been thought to be primary candidates for gene delivery in patients with pulmonary diseases. However, the tropism of AAVs in the lungs remains largely unknown.
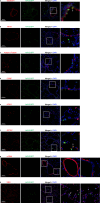
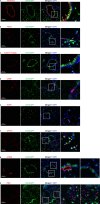
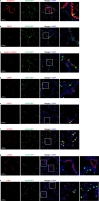
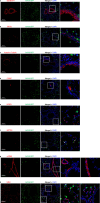
Results: Here, we investigate the tropism of twenty serotypes of AAVs by examining AAV-packed vector expression of the enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) in mice. AAV1, AAV4, AAV5, AAV6, AAV6.2, AAV-PHP.B, and AAV-PHP.S exhibit high transduction rates in the airway epithelium. AAV1, AAV4, AAV5, AAV6, and AAV6.2 highly infect club cells. AAV1, AAV4, AAV5, AAV6, AAV6.2, and AAV-PHP.B efficiently infect ciliated cells. AAV8 and AAVrh10 can infect a few alveolar type I cells. AAV1, AAV5, AAV6, AAV6.2, AAV9, and AAVie can infect alveolar type II cells. AAV1, AAV5, AAVie, AAV-PHP.B, AAV-PHP.eB, and AAV-PHP.S can infect a few endothelial cells. However, none of these AAVs can efficiently infect neuroendocrine or smooth muscle cells.
Conclusions: Our findings provide comprehensive information about the tropism of AAVs in pulmonary epithelium in mice, which might be helpful in developing efficient AAV-mediated gene therapy strategies for pulmonary disease treatment.
Keywords: Adeno-associated virus; Alveolar epithelial cells; Ciliated cells; Club cells; Tropism.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All authors agree to this publication. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Aneja MK, Geiger JP, Himmel A, Rudolph C. Targeted gene delivery to the lung. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2009;6:567–83. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Durinck S, Patel H, Foreman O, Mesh K, Eastham J, Caothien R, Newman RJ, Roose-Girma M, Darmanis S, Warming S, Lattanzi A, Liang Y, Haley B. Population-wide gene disruption in the murine lung epithelium via AAV-mediated delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 components. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2022;27:431–49. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Challis RC, Ravindra Kumar S, Chan KY, Challis C, Beadle K, Jang MJ, Kim HM, Rajendran PS, Tompkins JD, Shivkumar K, Deverman BE, Gradinaru V. Systemic AAV vectors for widespread and targeted gene delivery in rodents. Nat Protoc. 2019;14:379–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

