Effects of Bioprosthetic Valve Fracturing on Valve-in-Valve Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Transvalvular Gradients
- PMID: 39582677
- PMCID: PMC11584884
- DOI: 10.14503/THIJ-23-8304
Effects of Bioprosthetic Valve Fracturing on Valve-in-Valve Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Transvalvular Gradients
Abstract
Background: Valve-in-valve (ViV) transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) is quickly becoming a routine and effective means by which to treat degenerated bioprosthetic valves. A known complication of ViV-TAVI is patient-prosthesis mismatch, which substantially affects survival. Bioprosthetic valve fracture is a method by which to reduce the risk of patient-prosthesis mismatch and post-ViV-TAVI transvalvular gradients. This study sought to determine the safety and efficacy of post-ViV-TAVI bioprosthetic valve fracture.
Methods: Patients with a history of surgical aortic valve replacement undergoing ViV-TAVI bioprosthetic valve fracture (N = 25) at the corresponding institution from 2015 to 2022 were cataloged for a retrospective analysis. The implanted transcatheter valves were Medtronic Evolut R, Evolut PRO, and Evolut PRO+. Gradients were assessed before and after implantation and after fracturing using transthoracic echocardiogram.
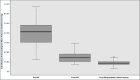
Results: The mean left ventricular ejection fraction of patients who underwent fracturing was 55.04%. The average (SD) peak and mean (SD) transvalvular gradients before the intervention were 68.17 (19.09) mm Hg and 38.98 (14.37) mm Hg, respectively. After ViV-TAVI, the same gradients were reduced to 27.25 (12.27) mm Hg and 15.63 (6.47) mm Hg, respectively. After bioprosthetic valve fracture, the gradients further decreased to 17.59 (7.93) mm Hg and 8.860 (3.334) mm Hg, respectively. The average reduction in peak gradient associated with fracturing was 12.07 mm Hg (95% CI, 5.73-18.41 mm Hg; P = .001). The average reduction in mean gradient associated with valve fracturing was 6.97 mm Hg (95% CI, 3.99-9.74 mm Hg; P < .001).
Conclusion: Bioprosthetic valve fracture is a viable option for reducing residual transvalvular gradients after ViV-TAVI and should be considered in patients with elevated gradients (>20 mm Hg) or with concern for patient-prosthesis mismatch in patients who have an unacceptable risk for a redo sternotomy and surgical aortic valve replacement.
Keywords: Transcatheter aortic valve replacement; balloon valvuloplasty; heart valve prosthesis.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by The Texas Heart Institute®.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Disclosure: The authors report no financial relationships or conflicts of interest regarding the content herein.
Figures
References
-
- Brennan JM, Edwards FH, Zhao Y, et al. DEcIDE AVR (Developing Evidence to Inform Decisions about Effectiveness–Aortic Valve Replacement) Research Team. Long-term safety and effectiveness of mechanical versus biologic aortic valve prostheses in older patients: results from the Society of Thoracic Surgeons Adult Cardiac Surgery National Database. Circulation. 2013;127(16):1647–1655. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.002003. doi: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Onorati F, Biancari F, De Feo M, et al. Mid-term results of aortic valve surgery in redo scenarios in the current practice: results from the multicentre European RECORD (REdo Cardiac Operation Research Database) initiative. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2015;47(2):269–280. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezu116. doi: - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

