The measurement of immunosuppressive drugs bymass spectrometry and immunoassay in a SouthAfrican transplant setting
- PMID: 39582744
- PMCID: PMC11585824
- DOI: 10.1016/j.plabm.2024.e00440
The measurement of immunosuppressive drugs bymass spectrometry and immunoassay in a SouthAfrican transplant setting
Abstract
Objectives: Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) is the gold standard for measurement of immunosuppressive drugs (ISDs), but is technically demanding and less accessible in resource-limited countries. Immunoassays can also measure ISD concentrations, but may be limited by cross-reactivity. We evaluated the performance of the Roche electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA) for cyclosporine, everolimus and sirolimus against LC-MS/MS in an African population for the first time.
Methods: Bias for ECLIA was estimated by comparing ECLIA-measured ISD concentrations to those obtained by LC-MS/MS in 42, 43 and 47 patient samples for cyclosporine, everolimus and sirolimus, respectively. Precision was assessed by performing replicate measurements of quality control materials.
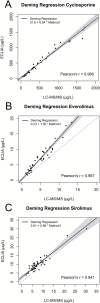
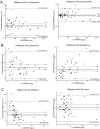
Results: Deming regression analysis for all ISDs showed strong correlation between ECLIA and LC-MS/MS with a Pearson's r of >0.94. The slopes for cyclosporine, everolimus and sirolimus were 0.94 [95 % CI: 0.87-1.03], 1.35 [95 % CI: 1.23-1.44] and 0.96 [95 % CI: 0.85-1.15] with y-intercepts of 31.60 μg/L [95 % CI: 2.02-57.63], 0.23 μg/L [95 % CI: 0.21 - 0.72] and 2.61 μg/L [95 % CI: 1.30-3.56], respectively. Difference plots showed a median bias of 2.07 % [95 % CI: 1.42 - 6.99 %], 41.2 % [95 % CI: 34.9-51.8 %] and 34.9 % [95 % CI: 28.4-47.3 %] for cyclosporine, everolimus and sirolimus, respectively.
Conclusions: The cyclosporine ECLIA yielded results comparable to LC-MS/MS while poorly comparable results were obtained for everolimus and sirolimus, which may be explained by ISD metabolite cross-reactivity, amongst other factors. The poor comparability, although not unique, is noteworthy and the clinical consequences of these differences require further investigation.
Keywords: Immunoassay; Immunosuppressants; Mass spectrometry; Therapeutic drug monitoring.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: The authors report that financial support was provided by the 10.13039/501100010753National Health Laboratory Service and 10.13039/100016545Roche Diagnostics. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported on this paper.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

