Choline Chloride-Urea Deep Eutectic Solvent/Cu-Mn Iminodiacetate Coordination Polymer as an Efficient Catalytic System for Synthesis of Morita-Baylis-Hillman Adducts with Antimicrobial Activity
- PMID: 39583655
- PMCID: PMC11579785
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c05386
Choline Chloride-Urea Deep Eutectic Solvent/Cu-Mn Iminodiacetate Coordination Polymer as an Efficient Catalytic System for Synthesis of Morita-Baylis-Hillman Adducts with Antimicrobial Activity
Abstract
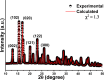
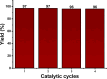
This work shows the synthesis of a series of Morita-Baylis-Hillman adducts from isatin derivatives via an efficient green approach involving the use of a new catalyst system, a mixture of copper-manganese iminodiacetate 1D coordination polymer (Cu/Mn-IDA) and choline chloride-urea deep eutectic solvent (ChCl/urea 1:2). The adducts 2a-2i were obtained in good to excellent yields (59-97%) with shorter reaction times. The results demonstrate for the first time the synergistic catalytic effect of the combination of deep eutectic solvent and coordination polymer on the Morita-Baylis-Hillman reactions. The catalyst recyclability was investigated, and it was found that Cu/Mn-IDA maintains consistent performance for at least four catalytic cycles. The synthesized compounds were evaluated for their in vitro antimicrobial activity against four bacteria and eight fungi species. Among all, 2a, 2b, 2d, 2e, and 2g showed antifungal and antibacterial activities in 70-83% of the strains tested. The adduct 2e exhibited significant antifungal activity with a minimum inhibitory concentration value of 128 μg mL-1 compared to the standard drug fluconazole (minimum inhibitory concentration, 256 μg mL-1).
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Saletti M.; Venditti J.; Paolino M.; Zacchei A.; Giuliani G.; Giorgi G.; Bonechi C.; Donati A.; Cappelli A. A Tri(Ethylene Glycol)-Tethered Morita-Baylis-Hillman Dimer in the Formation of Macrocyclic Crown Ether-Paracyclophane Hybrid Structures. RSC Adv. 2023, 13 (51), 35773–35780. 10.1039/D3RA06792K. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- da Câmara Rocha J.; da Franca Rodrigues K. A.; do Nascimento Néris P. L.; da Silva L. V.; Almeida F. S.; Lima V. S.; Peixoto R. F.; da Câmara Rocha J.; de Azevedo F. d. L. A. A.; Veras R. C.; de Medeiros I. A.; da Silva W. A. V.; Lima-Junior C. G.; de Almeida Vasconcellos M. L. A.; do Amaral I. P. G.; de Oliveira M. R.; de Souza Lima Keesen T. Biological Activity of Morita-Baylis-Hillman Adduct Homodimers in L. Infantum and L. Amazonensis: Anti-Leishmania Activity and Cytotoxicity. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118 (10), 3067–3076. 10.1007/s00436-019-06403-w. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Faheina-Martins G. V.; Leite J. A.; Dantas B. B.; Lima-Júnior C. G.; Vasconcellos M. L. A. A.; Rodrigues-Mascarenhas S.; Araújo D. A. M. Morita-Baylis-Hillman Adducts Display Anti-Inflammatory Effects by Modulating Inflammatory Mediator Expression in RAW264.7 Cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 1–9. 10.1155/2017/6898505. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
