Biological Activities and Chemical Contents of Edible Hohenbuehelia petaloides (Bull.) Schulzer
- PMID: 39583709
- PMCID: PMC11579941
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c02369
Biological Activities and Chemical Contents of Edible Hohenbuehelia petaloides (Bull.) Schulzer
Abstract
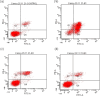
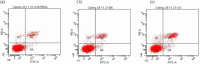
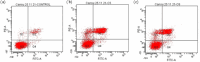
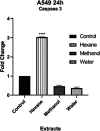
Mushrooms are a good diet with high protein and polyunsaturated fatty acid contents in health, food, and industry from past to present. Mushrooms have attracted a lot of attention in terms of the bioavailability of natural products. Hohenbuehelia petaloides, a member of the Pleuroteceae family, is an edible wood fungus that grows naturally on the trunks of old and decayed trees. In this study, the cytotoxic activities of hexane, methanol, and water extracts of H. petaloides against various cancer cell lines A549, MCF-7, PC-3, and HT-29 were investigated with the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-dipenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. In addition, the apoptotic, inflammatory, angiogenic, and antimicrobial effects of the extracts were examined by flow cytometry, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and well diffusion assays, respectively. Moreover, the antioxidant activity and phenolic and lipid components of H. petaloides were determined. The hexane extract showed the highest cytotoxic activity (IC50 = 26.48 ± 0.02 μg/mL) against A549 cells, while water and methanol extracts exhibited the highest cytotoxicity (IC50 = 83.18 ± 0.05 μg/mL and IC50 = 90.95 ± 0.05 μg/mL, respectively) against PC-3 cells. The hexane extract killed A549 cells via apoptosis. The methanol extract, at the IC50 level, was the most effective in decreasing both tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) release. In antioxidant activity tests performed with 5 different methods, the methanol extract had higher antioxidant activity than the others, followed by 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radical (IC50 = 82.61 ± 0.90 μg/mL) and 2,2-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) cation radical removal (IC50 = 55.20 ± 0.65 μg/mL) and CUPRAC-reducing power (IC50 = 76.41 ± 0.73 μg/mL). Among the extracts studied, the hexane extract showed antimicrobial activity against Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, and Micrococcus luteus with different inhibition zones. The major lipid components of H. petaloides analyzed by gas chromatography (GC) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC/MS) were elaidic acid (38.22%), palmitic acid (30.59%), stearic acid (13.21%), linoleic acid (4.35%), and azelaic acid (4.29%). The phenolic compounds determined by the high-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode-array detection (HPLC-DAD) system were p-hydroxybenzoic acid (7.42 μg/g extract), cinnamic acid (6.83 μg/g extract), gallic acid (5.36 μg/g extract), and protocatechuic acid (1.83 μg/g extract). The results showed that H. petaloides has the potential to be a natural source for the development of novel anticancer and antimicrobial agents as well as a beneficial food supplement for the prevention of cancer.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anti-hepatocarcinogenic and Anti-oxidant Effects of Mangrove Plant Scyphiphora hydrophyllacea.Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Jan;13(Suppl 1):S76-S83. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.203989. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 28479730 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Phenolic Compound, Gallic Acid from Sansevieria roxburghiana Schult and Schult. f. Rhizomes and Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Activities Evaluation.Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Oct;13(Suppl 3):S693-S699. doi: 10.4103/pm.pm_497_16. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 29142435 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Effect of Barringtonia racemosa and Hibiscus sabdariffa Fruit Extracts in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cell Line.Pharmacognosy Res. 2016 Jan-Mar;8(1):66-70. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.171104. Pharmacognosy Res. 2016. PMID: 26941539 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial, antioxidant and cytotoxic properties of Chenopodium glaucum L.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 29;16(10):e0255502. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255502. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2022 Aug 3;17(8):e0272181. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272181. PMID: 34714855 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Phytochemicals, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Potentials and LC-MS Analysis of Centaurea parviflora Desf. Extracts.Molecules. 2023 Feb 28;28(5):2263. doi: 10.3390/molecules28052263. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36903521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murugesan A. K.; Sathuvan M.; Javee A. PFL-lectin regulates the expression of apoptosis-related proteins to antecedent apoptosis in A549 and HT-29 cells. Adv. Cancer Biol.: Metastasis 2023, 7, 10009910.1016/j.adcanc.2023.100099. - DOI
-
- Öztürk M.; Tel-Cayan G.; Muhammad A.; Terzioglu P.; Duru M. E.. Mushrooms: A Source of Exciting Bioactive Compounds. In Studies in Natural Product Chemistry; Rahman A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2015; Vol. 45, pp 363–456.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
