Transforming agri-food value chains in Bangladesh: A practical application of blockchain for traceability and fair pricing
- PMID: 39583833
- PMCID: PMC11582413
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40091
Transforming agri-food value chains in Bangladesh: A practical application of blockchain for traceability and fair pricing
Abstract
The agricultural sector is a vital component of Bangladesh's economy, but its agri-food supply chain faces signifi-cant inefficiencies primarily due to the involvement of numerous intermediaries. This complexity not only reduces the profits for farmers but also affects the overall transparency and efficiency of the supply chain. This study aims to em-ploy blockchain technology to transform the traditional agri-food supply chain in Bangladesh, focusing on increasing transparency, enhancing efficiency, and improving profitability for farmers, thus potentially bolstering the entire agri-food ecosystem in the country. The research involves setting up a blockchain-based smart contract on the Ethereum Blockchain network. This approach guarantees that all transactions within the agri-food supply chain are transparent, traceable, and accountable. Additionally, the study develops a web application to facilitate user interaction with the smart contract, enhancing accessibility and usability. Performance analysis and testing of the implemented smart con-tract demonstrate its capability to handle a significant volume of transactions without compromising on performance. The solution effectively reduces the dependency on intermediaries, thereby increasing the profit margins for the farm-ers involved. The integration of blockchain technology in the agri-food supply chain has shown promising results in enhancing transparency and efficiency. It lays a solid foundation for future improvements and suggests a scalable model that could be applied to other sectors within the country to further enhance agricultural practices and economic growth.
Keywords: Agri-food value chain; Blockchain; Dapps; Ethereum; Smart contract; Traceability.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
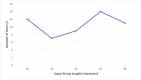
Figures
















References
-
- Rahman M.T. Role of agriculture in Bangladesh economy: uncovering the problems and challenges. Int. J. Bus. Manag. Invent. ISSN. 2017;6(July 2017):36–46. www.ijbmi.org [Online]. Available:
-
- Moyen Uddin M.M. 2015. “Causal Relationship between Agriculture, Industry and Services Sector for GDP Growth in Bangladesh: an Econo- Metric Investigation,”.
-
- Mondal M.H. Crop agriculture of Bangladesh: challenges and opportunities. Bangladesh J. Agric. Res. Aug. 2010;35(2):235–245.
-
- Das S., Munshi M.N., Kabir W. The impact of ICTs on agricultural production in Bangladesh: a study with food crops. SAARC J. Agric. 2017;14(2):78–89. doi: 10.3329/sja.v14i2.31247. - DOI
-
- Zhao G., et al. Blockchain technology in agri-food value chain management: a synthesis of applications, challenges and future research directions. Comput. Ind. 2019;109:83–99. doi: 10.1016/j.compind.2019.04.002. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

