Exosomal circular RNAs in tumor microenvironment: An emphasis on signaling pathways and clinical opportunities
- PMID: 39584047
- PMCID: PMC11586091
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.70019
Exosomal circular RNAs in tumor microenvironment: An emphasis on signaling pathways and clinical opportunities
Abstract
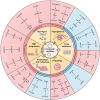
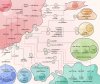
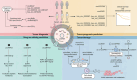
Exosomes can regulate the malignant progression of tumors by carrying a variety of genetic information and transmitting it to target cells. Recent studies indicate that exosomal circular RNAs (circRNAs) regulate multiple biological processes in carcinogenesis, such as tumor growth, metastasis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, drug resistance, autophagy, metabolism, angiogenesis, and immune escape. In the tumor microenvironment (TME), exosomal circRNAs can be transferred among tumor cells, endothelial cells, cancer-associated fibroblasts, immune cells, and microbiota, affecting tumor initiation and progression. Due to the high stability and widespread presence of exosomal circRNAs, they hold promise as biomarkers for tumor diagnosis and prognosis prediction in blood and urine. In addition, designing nanoparticles targeting exosomal circRNAs and utilizing exosomal circRNAs derived from immune cells or stem cells provide new strategies for cancer therapy. In this review, we examined the crucial role of exosomal circRNAs in regulating tumor-related signaling pathways and summarized the transmission of exosomal circRNAs between various types of cells and their impact on the TME. Finally, our review highlights the potential of exosomal circRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic prediction biomarkers, as well as suggesting new strategies for clinical therapy.
Keywords: biomarker; circRNA; exosome; tumor microenvironment; tumor therapy.
© 2024 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(3):229‐263. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(1):12‐49. - PubMed
-
- Schafer EJ, Jemal A, Wiese D, et al. Disparities and trends in genitourinary cancer incidence and mortality in the USA. Eur Urol. 2023;84(1):117‐126. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
