Developing a potent vaccine against Helicobacter pylori: critical considerations and challenges
- PMID: 39584502
- PMCID: PMC11964096
- DOI: 10.1017/erm.2024.19
Developing a potent vaccine against Helicobacter pylori: critical considerations and challenges
Abstract
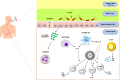
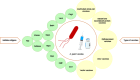
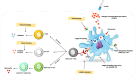
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is closely associated with gastric cancer and peptic ulcers. The effectiveness of antibiotic treatment against H. pylori is diminished by the emergence of drug-resistant strains, side effects, high cost and reinfections. Given the circumstances, it is imperative to develop a potent vaccination targeting H. pylori. Understanding H. pylori's pathogenicity and the host's immune response is essential to developing a vaccine. Furthermore, vaccine evaluation necessitates the careful selection of design formulation. This review article aims to provide a concise overview of the considerations involved in selecting the optimal antigen, adjuvant, vaccine delivery system and laboratory animal model for vaccine formulation. Furthermore, we will discuss some significant obstacles in the realm of developing a potent vaccination against H. pylori.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori vaccines; adjuvants; animal models; antigens; delivery system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any affiliations or financial ties with organisations or entities that have a financial interest or conflict related to the subject matter or materials covered in the paper.
Figures
References
-
- Hooi JKY, Lai WY, Ng WK, et al. (2017) Global Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 153, 420–429. - PubMed
-
- Rothenbacher D, Bode G, Berg G, et al. (1999) Helicobacter pylori among Preschool Children and Their Parents: Evidence of Parent-Child Transmission. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 179, 398–402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

