S2k guideline basal cell carcinoma of the skin (update 2023)
- PMID: 39584658
- PMCID: PMC11626229
- DOI: 10.1111/ddg.15566
S2k guideline basal cell carcinoma of the skin (update 2023)
Abstract
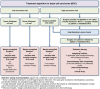
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common malignant tumor in the fair-skinned population and its incidence continues to rise. An update of the S2k guideline with the participation of all specialist societies familiar with the clinical picture and previous literature research is of great importance for the quality of care for affected patients. In addition to epidemiology, diagnostics and histology are discussed. After risk stratification, therapy is divided into topical, systemic and radiation therapy. Surgical removal remains the treatment of first choice in most cases. The approval of anti-PD1 inhibitors for locally advanced and metastatic tumors has opened up a new option in second-line therapy (after hedgehog inhibitors).
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Deutsche Dermatologische Gesellschaft.
Conflict of interest statement
Please refer to the AWMF guideline report available online.
Figures
References
-
- Lomas A, Leonardi‐Bee J, Bath‐Hextall F. A systematic review of worldwide incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Br J Dermatol 2012; 166: 1069‐80 - PubMed
-
- Kossard S, Epstein EH, Cerio J, et al. Basal cell carcinoma. In: LeBoit PE, Burg G, Weedon D, Sarasin A: Skin Tumours: Pathology and Genetics. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. IARC Press, 2006; 13‐20
-
- Krebs in Deutschland für 2013/2014. 11. Ausgabe. Robert Koch‐Institut (Hrsg) und die Gesellschaft der epidemiologischen Krebsregister in Deutschland e.V. (Hrsg). Berlin, 2017. (DOI: 10.17886/rkipubl-2017-007) - DOI
-
- Krebsregister RLP Bericht 2017: Nicht‐melanozytäre Hauttumore (C44), https://www.krebsregister‐rlp.de/fileadmin/user_upload/C44_2017.pdf “accessed on December 1, 2023“
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical