Optimizing US for HCC surveillance
- PMID: 39585379
- PMCID: PMC12069441
- DOI: 10.1007/s00261-024-04631-y
Optimizing US for HCC surveillance
Abstract
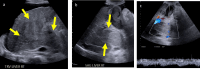
Ultrasound is the primary imaging modality used for surveillance of patients at risk for HCC. In 2017, the American College of Radiology Liver Imaging Reporting and Data Systems (ACR LI-RADS) introduced US LI-RADS to standardize the performance, interpretation, and reporting of US for HCC surveillance, with the algorithm recently updated as LI-RADS US Surveillance v2024. The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) recommends reporting both the examination-level LI-RADS US Category as well as the US Visualization Score. The US Category conveys the overall findings of the exam and primarily determines follow up recommendations. The US Visualization Score conveys the expected sensitivity of the test and stratifies patients into appropriate surveillance pathways. One of the goals of routine surveillance is the detection of HCC at an early, potentially curable stage. Therefore, optimizing US technique is of critical importance. Increasing North American and worldwide utilization of LI-RADS US Surveillance, which includes technical recommendations, through education and outreach will undoubtedly benefit patients undergoing US HCC surveillance.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interest: SKR: Elsevier, book royalties DF: Research support GE Healthcare, Philips Healthcare and Siemens Healthineers, member of expert medical advisory board Philips Healthcare, research equipment loan GE Healthcare, Philips Healthcare and Siemens Healthineers AK: Elsevier, book royalties, research support Canon Medical Systems CF: Honoraria College of Physicians and Surgeons of Alberta as elected council member for Provincial College; shareholder Mikata Health; partner radiologist Medical Imaging Consultants.
Figures

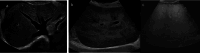
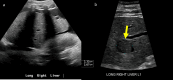
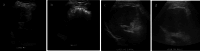

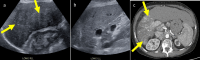


References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(3):229-263. 10.3322/caac.21834 - PubMed
-
- Yang B, Zhang B, Xu Y, et al. Prospective study of early detection for primary liver cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1997;123(6):357-360. 10.1007/BF01438313 - PubMed
-
- Zhang BH, Yang BH, Tang ZY. Randomized controlled trial of screening for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004;130(7):417-422. 10.1007/s00432-004-0552-0 - PubMed
-
- Fetzer DT, Rodgers SK, Harris AC, et al. Screening and Surveillance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Introduction to Ultrasound Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System. Radiol Clin North Am. 2017;55(6). 10.1016/j.rcl.2017.06.012 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

