Generation of short-term follow-up chest CT images using a latent diffusion model in COVID-19
- PMID: 39585556
- PMCID: PMC11953082
- DOI: 10.1007/s11604-024-01699-w
Generation of short-term follow-up chest CT images using a latent diffusion model in COVID-19
Abstract
Purpose: Despite a global decrease in the number of COVID-19 patients, early prediction of the clinical course for optimal patient care remains challenging. Recently, the usefulness of image generation for medical images has been investigated. This study aimed to generate short-term follow-up chest CT images using a latent diffusion model in patients with COVID-19.
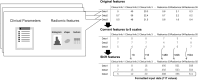
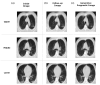
Materials and methods: We retrospectively enrolled 505 patients with COVID-19 for whom the clinical parameters (patient background, clinical symptoms, and blood test results) upon admission were available and chest CT imaging was performed. Subject datasets (n = 505) were allocated for training (n = 403), and the remaining (n = 102) were reserved for evaluation. The image underwent variational autoencoder (VAE) encoding, resulting in latent vectors. The information consisting of initial clinical parameters and radiomic features were formatted as a table data encoder. Initial and follow-up latent vectors and the initial table data encoders were utilized for training the diffusion model. The evaluation data were used to generate prognostic images. Then, similarity of the prognostic images (generated images) and the follow-up images (real images) was evaluated by zero-mean normalized cross-correlation (ZNCC), peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), and structural similarity (SSIM). Visual assessment was also performed using a numerical rating scale.
Results: Prognostic chest CT images were generated using the diffusion model. Image similarity showed reasonable values of 0.973 ± 0.028 for the ZNCC, 24.48 ± 3.46 for the PSNR, and 0.844 ± 0.075 for the SSIM. Visual evaluation of the images by two pulmonologists and one radiologist yielded a reasonable mean score.
Conclusions: The similarity and validity of generated predictive images for the course of COVID-19-associated pneumonia using a diffusion model were reasonable. The generation of prognostic images may suggest potential utility for early prediction of the clinical course in COVID-19-associated pneumonia and other respiratory diseases.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chest CT images; Deep learning; Latent diffusion model; Prognostic image generation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Ethical statement: This retrospective multicenter study was approved by the Institutional Review Boards of Chiba University (No. 4074 Date 2021/11/24) and Chiba Aoba Municipal Hospital (No. 20200301). The study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The institutional review boards of all hospital institutions included in the present study provided ethical approval. The requirement for written informed consent was waived due to the characteristics of the retrospective study.
Figures


References
-
- WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports.Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports. World Health Organization; 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019.
-
- Ranney ML, Griffeth V, Jha AK. Critical supply shortages - the need for ventilators and personal protective equipment during the Covid-19 pandemic. N Engl J Med. 2020;382: e41. - PubMed
-
- LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015;521:436–44. - PubMed
-
- Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, Setio AAA, Ciompi F, Ghafoorian M, et al. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Image Anal. 2017;42:60–88. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

