Trim72 is a major host factor protecting against lethal Candida albicans infection
- PMID: 39585917
- PMCID: PMC11627414
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012747
Trim72 is a major host factor protecting against lethal Candida albicans infection
Abstract
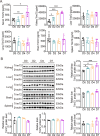
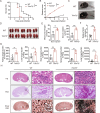
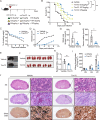
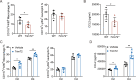
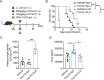
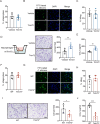
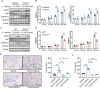
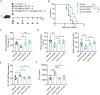
Candida albicans is the most common aetiologic pathogen of fungal infections associated with high mortality in immunocompromised patients. There is an urgent need to develop new antifungal therapies owing to the poor efficacy and resistance of current antifungals. Here, we report that Trim72 positively regulates antifungal immunity during lethal fungal infection. Trim72 levels are significantly increased after Candida albicans infection. In vivo, Trim72 knockout significantly increases mortality, organ fungal burden and kidney damage in mice after lethal Candida albicans infection. Whereas recombinant Trim72 protein treatment protects mice against invasive candidiasis. Mechanistically, Trim72 facilitates macrophage infiltration and CCL2 production, which mediates Trim72-elicited protection against lethal Candida albicans infection. Furthermore, Trim72 may enhance macrophage migration and CCL2 production via NF-κB and ERK1/2 signaling. Inhibition of NF-κB and ERK1/2 signaling abrogates Trim72-mediated protection against lethal Candida albicans infection. Therefore, these data imply that Trim72 may be developed as a host-directed therapy for treating severe systemic candidiasis.
Copyright: © 2024 Tan et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Myeloid cell deficiency of p38γ/p38δ protects against candidiasis and regulates antifungal immunity.EMBO Mol Med. 2018 May;10(5):e8485. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201708485. EMBO Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29661910 Free PMC article.
-
AIM2 enhances Candida albicans infection through promoting macrophage apoptosis via AKT signaling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Jun 25;81(1):280. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05326-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38918243 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammasome-mediated GSDMD activation facilitates escape of Candida albicans from macrophages.Nat Commun. 2021 Nov 18;12(1):6699. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27034-9. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34795266 Free PMC article.
-
Candidiasis: From cutaneous to systemic, new perspectives of potential targets and therapeutic strategies.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023 Aug;199:114960. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2023.114960. Epub 2023 Jun 10. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023. PMID: 37307922 Review.
-
Modulating Host Signaling Pathways to Promote Resistance to Infection by Candida albicans.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Nov 21;7:481. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00481. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29201860 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang YC, Tsai IC, Lin C, Hsieh WP, Lan CY, Chuang YJ, et al.. Essential functional modules for pathogenic and defensive mechanisms in Candida albicans infections. BioMed research international. 2014;2014:136130. Epub 2014/04/24. doi: 10.1155/2014/136130 24757665; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3976935. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

