Inceptor binds to and directs insulin towards lysosomal degradation in β cells
- PMID: 39587340
- PMCID: PMC11659164
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-024-01164-y
Inceptor binds to and directs insulin towards lysosomal degradation in β cells
Abstract
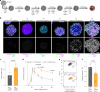
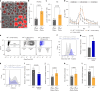
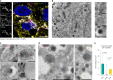
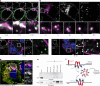
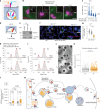
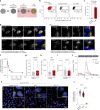
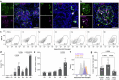
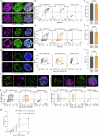
Blunted first-phase insulin secretion and insulin deficiency are indicators of β cell dysfunction and diabetes manifestation. Therefore, insights into molecular mechanisms that regulate insulin homeostasis might provide entry sites to replenish insulin content and restore β cell function. Here, we identify the insulin inhibitory receptor (inceptor; encoded by the gene IIR/ELAPOR1) as an insulin-binding receptor that regulates insulin stores by lysosomal degradation. Using human induced pluripotent stem cell (SC)-derived islets, we show that IIR knockout (KO) results in enhanced SC β cell differentiation and survival. Strikingly, extended in vitro culture of IIR KO SC β cells leads to greatly increased insulin content and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS). We find that inceptor localizes to clathrin-coated vesicles close to the plasma membrane and in the trans-Golgi network as well as in secretory granules, where it acts as a sorting receptor to direct proinsulin and insulin towards lysosomal degradation. Targeting inceptor using a monoclonal antibody increases proinsulin and insulin content and improves SC β cell GSIS. Altogether, our findings reveal the basic mechanisms of β cell insulin turnover and identify inceptor as an insulin degradation receptor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: H.L. is the inventor of the patent ‘Novel IGFR-like receptor and uses thereof’ held by the Helmholtz Zentrum München (WO2017042242) and co-inventor of the pending patent application filed by the Helmholtz Zentrum München ‘Novel IGFR-like 1 monoclonal antibodies and uses thereof’ (WO2023002060). The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

