ILF2 protein is a promising serum biomarker for early detection of gastric cancer
- PMID: 39587551
- PMCID: PMC11587746
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-13205-6
ILF2 protein is a promising serum biomarker for early detection of gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: Our previous small-sample study indicated that serum levels of interleukin enhancer binding factor 2 (ILF2) may have the potential for gastric cancer (GC) detection. The present study was conducted to further validate the diagnostic value of serum ILF2 protein for GC.
Methods: Serum specimens and clinical data were collected from patients with GC (n = 99) or benign gastric disease (BGD) (n = 49) and healthy controls (HC) (n = 51). Serum ILF2 levels were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The diagnostic performance of ILF2 was evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). The independence and synergy of ILF2 in GC diagnosis were analyzed by modeling with conventional blood indicators.
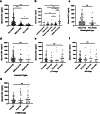
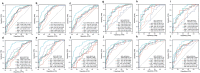
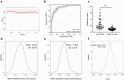
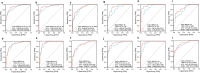
Results: The median serum ILF2 level was higher in the GC group (227.8ng/mL) than in the BGD group (72.0ng/mL) and the HC group (56.8ng/mL) (p < 0.001), and no significant difference across GC subgroups. The AUCs of ILF2 were 0.915 (95%CI 0.873-0.957) for GC vs. HC, 0.854 (95%CI 0.793-0.915) for GC vs. BGD, 0.885 (95%CI 0.841-0.929) for GC vs. BGD + HC, and 0.888 (95% CI 0.830-0.945) for TNM I stage GC vs. BGD + HC, outperforming conventional blood indicators (corresponding AUCs ranging from 0.641 to 0.782). ILF2 was independent of and synergistic with conventional blood indicators in GC diagnosis, and a simple diagnostic model based on ILF2 and red blood cell count improved the diagnostic performance, with positive rates of approximately 90% in various subgroups of GC.
Conclusions: Serum ILF2 protein is a novel and potential serum biomarker for the detection of GC, especially for early GC.
Keywords: Early diagnosis; Gastric cancer; ILF2; Serum biomarker.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This research was approved by the Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University. All examinations in humans were conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki and its amendments. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were approved by the Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. The Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University waived the requirement for patient informed consent because the assay for ILF2 used previously collected frozen leftover serum specimens from biochemical assays, not specifically drawn blood specimens. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
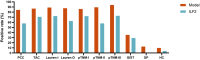
References
-
- Dooley CP, Larson AW, Stace NH, Renner IG, Valenzuela JE, Eliasoph J et al. Double-contrast barium meal and upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. A comparative study. ANN INTERN MED. 1984 1984/10/1;101(4):538 – 45. - PubMed
-
- Xu Y, Zhang P, Zhang K, Huang C. The application of CA72-4 in the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of gastric cancer. BBA-REV CANCER. 2021;1876(2):188634. 2021/12/1. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

