A Novel Synonymous Variant in SQSTM1 Causes Neurodegeneration With Ataxia, Dystonia, and Gaze Palsy Revealed by Urine-Derived Cells-Based Functional Analysis
- PMID: 39587727
- PMCID: PMC11588856
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.70044
A Novel Synonymous Variant in SQSTM1 Causes Neurodegeneration With Ataxia, Dystonia, and Gaze Palsy Revealed by Urine-Derived Cells-Based Functional Analysis
Abstract
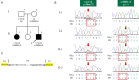
Background: Heterozygous variants of sequestosome-1 gene (SQSTM1) have been reported in patients with various neurological disorders, whereas biallelic pathogenic variants of SQSTM1 can cause child-onset and multisystem neurodegeneration, including cerebellar ataxia, dystonia, and vertical gaze palsy (NADGP). Here, we describe two cases of NADGP in a Japanese family.
Methods: We performed clinical and genetic laboratory evaluations of the two patients and their healthy parents.
Results: By whole-exome sequencing, we identified compound heterozygous variants in SQSTM1(NM_003900.5): c.1A>G p.(Met1?) in the initial codon, and c.969G>A, located at the 3' end of exon 6, which is novel and seemingly a synonymous but is actually a truncating variant causing aberrant splicing. An SQSTM1 protein expression assay using urine-derived cells (UDCs) demonstrated that both variants (c.1A>G and c.969G>A) were unable to induce normal splicing of premessenger RNA. Cerebellar ataxia is a characteristic manifestation of this disorder; however, brain magnetic resonance imaging studies have not shown significant cerebellar atrophy. Our patients experienced chorea during adolescence.
Conclusions: Only a few reports have highlighted the presence of chorea; however, our findings suggest that NADGP should be considered as a differential diagnosis of hereditary chorea. This study also demonstrates the utility of UDCs, obtained using noninvasive approaches, in functionally analyzing genetic diseases.
Keywords: GC‐AT intron; NADGP; SQSTM1; UDC; urine‐derived cell.
© 2024 The Author(s). Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Homozygous SQSTM1 nonsense variant identified in a patient with brainstem involvement.Brain Dev. 2021 Nov;43(10):1039-1043. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2021.06.001. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Brain Dev. 2021. PMID: 34147300
-
Homozygous sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1) mutation: a rare cause for childhood-onset progressive cerebellar ataxia with vertical gaze palsy.Ophthalmic Genet. 2019 Aug;40(4):376-379. doi: 10.1080/13816810.2019.1666414. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Ophthalmic Genet. 2019. PMID: 31525130
-
A Novel Variant in SQSTM1 Gene Causing Neurodegeneration with Ataxia, Dystonia, and Gaze Palsy in a Peruvian Family.Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2024 Jun;11(6):746-748. doi: 10.1002/mdc3.14025. Epub 2024 Mar 26. Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 38532471 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
SQSTM1 mutation: Description of the first Tunisian case and literature review.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Dec;8(12):e1543. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1543. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. PMID: 33135846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SQSTM1 variant in disorders of the frontotemporal dementia-amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spectrum: identification of a novel heterozygous variant and a review of the literature.J Neurol. 2021 Apr;268(4):1351-1357. doi: 10.1007/s00415-020-10283-x. Epub 2020 Oct 30. J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33125541 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- JP22K15646/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- JP23K27520/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- JP24K02230/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- JP24K10637/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- JPMH23FC1010/Health Labour Sciences Research Grant from Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
- JP23dk0207066h0001/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JP24dk0207066h0002/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JP24ek0109617/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JP24ek0109648/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JP24ek0109674/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JP24ek0109677/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- JP24ek0109760/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

