Revisiting the Atrioventricular Conduction Axis for the 21st Century
- PMID: 39588052
- PMCID: PMC11588108
- DOI: 10.15420/aer.2024.15
Revisiting the Atrioventricular Conduction Axis for the 21st Century
Abstract
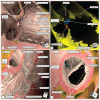
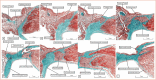
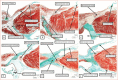
In this review, we summarise the ongoing debate surrounding the anatomy of the atrioventricular conduction axis and its relevance to pacing. We highlight previous disagreements and emphasise the importance of understanding the anatomical location of the axis. We give credit and support to the initial descriptions by His and Tawara, in particular their attention to the relationship of the atrioventricular conduction axis with the membranous septum. We express our disagreements with recent diagrams that incorrectly, in our opinion, depict the left bundle and right bundle branches. We offer our own latest understanding of the location and relationships of the atrioventricular conduction axis, including details of its development, and differences between human and animal hearts. We also emphasise the importance of understanding the relationship between the inferior pyramidal space and the inferoseptal recess so as appropriately to place the axis within the heart. We conclude by emphasising the need to consider the heart in the context of the body, describing its component parts by using attitudinally appropriate nomenclature.
Keywords: Atrioventricular node; bundle of His; left bundle branch; right bundle branch.
Copyright © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Radcliffe Group Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: RHA is on the Arrhythmia & Electrophysiology Review editorial board; this did not affect peer review. All other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures





References
-
- His W Jr. Die Thatigkeit des embryonalen Herzens und deren Bedeutung für die Lehre von der Herzbewegung beim Erwachsenen. Arb Med Klin Leipzig. 1893;1:14–49.
-
- Tawara S. Jena: Gustav Fischer, 1906: Das Reizleitungssystem des Säugetierherzens: eine anatomisch-histologische Studie über das Atrioventrikularbundel und die Purkinjeschen Fäden.
-
- McAlpine WA. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1975;34–35.: Heart and Coronary Arteries. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

