STK39-mediated amplification of γ-H2A.X promotes homologous recombination and contributes to PARP inhibitor resistance
- PMID: 39588777
- PMCID: PMC11662673
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1099
STK39-mediated amplification of γ-H2A.X promotes homologous recombination and contributes to PARP inhibitor resistance
Abstract
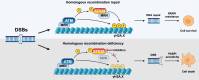
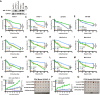
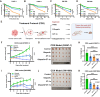
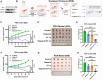
The phosphorylation of histone H2A.X into γH2A.X is a crucial early event in the DNA damage response, marking DNA damage sites and initiating repair processes. While ATM kinase is traditionally recognized as the primary mediator of H2A.X phosphorylation, our study identifies serine/threonine kinase 39 (STK39) as a novel enhancer of this critical signaling pathway. We demonstrate that after DNA damage, STK39 undergoes phosphorylation by the ATM kinase, facilitating its interaction with the Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 complex and subsequent recruitment to chromatin. This recruitment enables STK39 to further phosphorylate H2A.X, thus amplifying γH2A.X production and promoting homologous recombination repair. Notably, we observe a significant upregulation of STK39 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAAD) tissues, correlating with heightened resistance to PARPi therapy. Furthermore, we demonstrate the synergistic efficacy of combining STK39 inhibition with PARP inhibitors in suppressing and reversing PAAD growth. This study not only provides new insights into the molecular dynamics of H2A.X phosphorylation but also highlights the therapeutic potential of targeting STK39 to enhance PARPi sensitivity in PAAD (created with BioRender).
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
-
- Dobbelstein M., Sørensen C.S.. Exploiting replicative stress to treat cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015; 14:405–423. - PubMed
-
- Lee J.-H., Paull T.T.. ATM activation by DNA double-strand breaks through the Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 complex. Science. 2005; 308:551–554. - PubMed
-
- Lee J.-H., Paull T.T.. Activation and regulation of ATM kinase activity in response to DNA double-strand breaks. Oncogene. 2007; 26:7741–7748. - PubMed
-
- Stewart G.S., Wang B., Bignell C.R., Taylor A.M.R., Elledge S.J.. MDC1 is a mediator of the mammalian DNA damage checkpoint. Nature. 2003; 421:961–966. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2023ZD0502200/National Science and Technology Major Project
- 82272757/National Science Foundation of China
- 2021-RC310-013/Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences
- 2021-I2M-1-067/Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences
- LC2021R02/Cancer Foundation of China
- 2022-CICAMS-80102022203/National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding
- Medical Health Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Provincial Health
- Q22H168103/Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation
- CFA202201008/Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences
- 3332022028,2023-CICAMS-3332023029/Peking Union Medical College
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

