ARID1A governs the silencing of sex-linked transcription during male meiosis in the mouse
- PMID: 39589400
- PMCID: PMC11594533
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.88024
ARID1A governs the silencing of sex-linked transcription during male meiosis in the mouse
Abstract
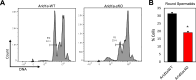
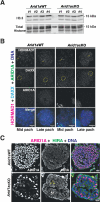
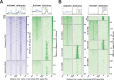
We present evidence implicating the BAF (BRG1/BRM Associated Factor) chromatin remodeler in meiotic sex chromosome inactivation (MSCI). By immunofluorescence (IF), the putative BAF DNA binding subunit, ARID1A (AT-rich Interaction Domain 1 a), appeared enriched on the male sex chromosomes during diplonema of meiosis I. Germ cells showing a Cre-induced loss of ARID1A arrested in pachynema and failed to repress sex-linked genes, indicating a defective MSCI. Mutant sex chromosomes displayed an abnormal presence of elongating RNA polymerase II coupled with an overall increase in chromatin accessibility detectable by ATAC-seq. We identified a role for ARID1A in promoting the preferential enrichment of the histone variant, H3.3, on the sex chromosomes, a known hallmark of MSCI. Without ARID1A, the sex chromosomes appeared depleted of H3.3 at levels resembling autosomes. Higher resolution analyses by CUT&RUN revealed shifts in sex-linked H3.3 associations from discrete intergenic sites and broader gene-body domains to promoters in response to the loss of ARID1A. Several sex-linked sites displayed ectopic H3.3 occupancy that did not co-localize with DMC1 (DNA meiotic recombinase 1). This observation suggests a requirement for ARID1A in DMC1 localization to the asynapsed sex chromatids. We conclude that ARID1A-directed H3.3 localization influences meiotic sex chromosome gene regulation and DNA repair.
Keywords: ARID1A; Mouse; chromatin remodelers; developmental biology; gene regulation; genetics; genomics; meiotic sex chromosome; mouse; sex-linked DNA repair; spermatogenesis.
© 2023, Menon et al.
Conflict of interest statement
DM, PC, NM, TM No competing interests declared
Figures

















Update of
-
ARID1A governs the silencing of sex-linked transcription during male meiosis in the mouse.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 28:2023.05.25.542290. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.25.542290. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2024 Nov 26;12:RP88024. doi: 10.7554/eLife.88024. PMID: 37292940 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Alexander AK, Rice EJ, Lujic J, Simon LE, Tanis S, Barshad G, Zhu L, Lama J, Cohen PE, Danko CG. A-MYB and BRDT-dependent RNA Polymerase II pause release orchestrates transcriptional regulation in mammalian meiosis. Nature Communications. 2023;14:1753. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37408-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baarends WM, Wassenaar E, van der Laan R, Hoogerbrugge J, Sleddens-Linkels E, Hoeijmakers JHJ, de Boer P, Grootegoed JA. Silencing of unpaired chromatin and histone H2A ubiquitination in mammalian meiosis. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2005;25:1041–1053. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.3.1041-1053.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

