Enhanced Detection of Vibrio harveyi Using a Dual-Composite DNAzyme-Based Biosensor
- PMID: 39590007
- PMCID: PMC11591735
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14110548
Enhanced Detection of Vibrio harveyi Using a Dual-Composite DNAzyme-Based Biosensor
Abstract
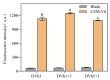
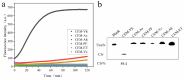
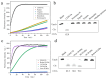
Vibrio harveyi is a serious bacterial pathogen which can infect a wide range of marine organisms, such as marine fish, invertebrates, and shrimp, in aquaculture, causing severe losses. In addition, V. harveyi can be transmitted through food and water, infecting humans and posing a serious threat to public safety. Therefore, rapid and accurate detection of this pathogen is key for the prevention and control of related diseases. In this study, nine rounds of in vitro screening were conducted with Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment (SELEX) technology using unmodified DNA libraries, targeting the crude extracellular matrix (CEM) of V. harveyi. Two DNAzymes, named DVh1 and DVh3, with high activity and specificity were obtained. Furthermore, a fluorescent biosensor with dual DNAzymes was constructed which exhibited improved detection efficiency. The sensor showed a good fluorescence response to multiple aquatic products (i.e., fish, shrimp, and shellfish) infected with V. harveyi, with a detection limit below 11 CFU/mL. The fluorescence signal was observed within 30 min of reaction after target addition. This simple, inexpensive, highly effective, and easy to operate DNAzymes biosensor can be used for field detection of V. harveyi.
Keywords: SELEX; Vibrio harveyi; dual DNAzyme; field detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there is no conflict of interests regarding this paper.
Figures








References
-
- Dubert J., Nelson D.R., Spinard E.J., Kessner L., Gomez-Chiarri M., Costa F.d., Prado S., Barja J.L. Following the infection process of vibriosis in Manila clam (Ruditapes philippinarum) larvae through GFP-tagged pathogenic Vibrio species. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016;133:27–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2015.11.008. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

