Clinical Outcome Patterns of Use of Radium-223 in Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 39590111
- PMCID: PMC11592830
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol31110480
Clinical Outcome Patterns of Use of Radium-223 in Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Abstract
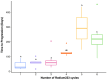
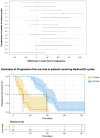
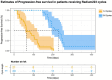
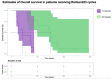
Introduction: Radium-223 dichloride (radium-223) is a bone-targeting radioisotope therapy that aids in the survival of patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) to bones. This study aimed to describe the clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with mCRPC treated with radium-223 in a real-world setting. Methods: This was a retrospective study of patients with mCRPC treated with radium-223 between 2016 and 2020 at the London Health Sciences Centre in London, Canada. The baseline characteristics between the patients receiving 1-3 and 4-6 treatment cycles were compared using a two-sample t-test and Chi-square test. ANOVA was used to determine if there was a difference in each diagnostic variable per treatment cycle. Kaplan-Meier curves were generated to estimate progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival in the patients treated with different numbers of cycles. Results: Fifty eligible patients were identified. The median age was 71 years (IQR: 66-76). Most patients (62%) received radium-223 beyond the third-line treatment. The mean number of radium-223 treatments was four. While 60% of the patients received 4-6 injections, 40% received 1-3 injections. Fifty-eight percent (58%) of the patients demonstrated a clinical benefit, with the remainder expressing either disease progression (28%) or stable disease (10%). The patients treated with 4-6 cycles had a delay to disease progression compared to those given 1-3 cycles of radium-223 (F5,35 = 10.52, p < 0.001). A higher alkaline phosphatase level prior to treatment was associated with a longer PFS (z33 = 2.362, p = 0.018). Treatment-related hospitalization for skeletal-related events was noted in 8% of the patients, and 14% required treatment discontinuation due to hematologic toxicity. Conclusions: This study confirms the safety of radium-223 in patients with mCRPC in a real-world setting. The radium-223 treatment was associated with a clinical benefit in the majority of the patients, particularly in those with higher pre-treatment serum alkaline phosphatase levels. Further studies to identify the predictive biomarkers are warranted to better guide the contemporary use of radium-223.
Keywords: bone metastasis; castration-resistant prostate cancer; clinical outcomes; radium-223.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests. Ricardo Fernandes has the following disclosures: Advisory Board Member or Honoraria: Merck, Novartis, Janssen, Pfizer, BMS, Ipsen, and Bayer; Travel Grant: Janssen. The other authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Sharifi N., Gulley J.L., Dahut W.L. Androgen Deprivation Therapy for Prostate Cancer. [(accessed on 4 July 2024)];J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2005 294:238–244. doi: 10.1001/jama.294.2.238. Available online: https://jamanetwork.com/ - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

