Detecting Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer in PI-RADS 3 Lesions Using T2w-Derived Radiomics Feature Maps in 3T Prostate MRI
- PMID: 39590134
- PMCID: PMC11592716
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol31110503
Detecting Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer in PI-RADS 3 Lesions Using T2w-Derived Radiomics Feature Maps in 3T Prostate MRI
Abstract
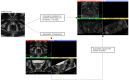
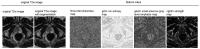
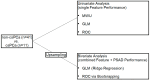
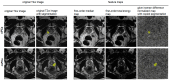
Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System version 2.1 (PI-RADS) category 3 lesions are a challenge in the clinical workflow. A better detection of the infrequently occurring clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa) in PI-RADS 3 lesions is an important objective. The purpose of this study was to evaluate if feature maps calculated from T2-weighted (T2w) 3 Tesla (3T) MRI can help detect csPCa in PI-RADS category 3 lesions. In-house biparametric 3T prostate MRI examinations acquired between January 2019 and June 2023 because of elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels were retrospectively screened. Inclusion criteria were a PI-RADS 3 lesion and available results of an ultrasound-guided targeted and systematic biopsy. Exclusion criteria were a simultaneous PI-RADS category 4 or 5 lesion and hip replacement. Target lesions with the International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grade group 1 were rated clinically insignificant PCa (ciPCa) and ≥2 csPCa. This resulted in 52 patients being included in the final analysis, of whom 11 (21.1%), 8 (15.4%), and 33 (63.5%) patients had csPCa, ciPCa, and no PCa, respectively, with the latter two groups being combined as non-csPCa. Eight of the csPCas were located in the peripheral zone (PZ) and three in the transition zone (TZ). In the non-csPCa group, 29 were located in the PZ and 12 in the TZ. Target lesions were marked with volumes of interest (VOIs) on axial T2w images. Axial T2w images were then converted to 93 feature maps. VOIs were copied into the maps, and feature quantity was retrieved directly. Features were tested for significant differences with the Mann-Whitney U-test. Univariate models for single feature performance and bivariate models implementing PSA density (PSAD) were calculated. Ten map-derived features differed significantly between the csPCa and non-csPCa groups (AUCs: 0.70-0.84). The diagnostic performance for TZ lesions (AUC: 0.83-1.00) was superior to PZ lesions (AUC: 0.74-0.85). In the bivariate models, performance in the PZ improved with AUCs >0.90 throughout. Parametric feature maps alone and as bivariate models with PSAD can (?) noninvasively identify csPCa in PI-RADS 3 lesions and could serve as a quantitative tool reducing ambiguity in PI-RADS 3 lesions.
Keywords: magnetic resonance imaging; prostate; prostatic neoplasms; prostatitis; radiomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. One of the authors, Professor Bernd Hamm, receives grants for the Department of Radiology from Abbott, AbbVie, Ablative Solutions, Accovion, Achogen Inc., Actelion Pharmaceuticals, ADIR, Aesculap, Agios Pharmaceuticals, INC., AGO, AIF: Arbeitsgemeinschaft industrieller Forschungsvereinigungen, AIO: Arbeitsgemeinschaft internistische Onkologie, Aktionsbündnis Partnersicherheit e.V., Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Amgen, AO Foundation, Aravive, Arena Pharmaceuticals, ARMO Biosciences, Inc., Array Biopharma Inc., Art photonics GmbH Berlin, ASAS, Ascelia Pharma AB, Ascendis, ASR Advanced sleep research, Astrellas, AstraZeneca, August Research OOF, Sofia, BG, BARD, Basiliea, Bayer Healthcare, Bayer Schering Pharma, Bayer Vital, BBraun, BerGenBioASA, Berlin-Brandenburger Centrum für regenerative Therapie (BCRT), Berliner Krebsgesellschaft, Biontech Mainz, BioNTech SE, Biotronik, Bioven, BMBF, BMS, Boehring Ingelheimer, Boston Biomedical Inc., Boston Scientific Medizintechnik GmbH, BRACCO Group, Brahms GmbH, Brainsgate, Bistol-Myers Squibb, Calithera Biosciences UK, Cantargia AB, Medicon Village, Cascadian Therapeutics, Inc., Celgene, CELLACT Pharma, Celldex Therapeutics, Cellestia Biotech AG CH, CeloNova BioSciences, Charité research organization GmbH, Chiltern, CLOVIS ONCOLOGY, INC., Covance, CRO Charité, CTI Ulm, CUBIST, CureVac AG, Tübingen, Curis, Daiichi Sankyo, Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH, USA, DC Devices, Inc. USA, Delcath Systems, Dermira Inc., Deutsche Krebshilfe, Deutsche Rheuma Liga, DZ—Deutsche Diabetes Forschungsgesellschaft e.V., Deutsches Zentrum für Luft-und Raumfahrt e.V., DFG, Dr. Falk Pharma GmbH, DSM Nutritional Products AG, Dt. Gesellschaft für muskuloskelettale Radiologie, Dt. Stiftung für Herzforschung, Dynavax, Aisai Ltd., European Knowledge Centre, Mosquito Way, Hatfield, Eli Lilly and Company Ltd., EORTC, Episurf Medical, Epizyme, Inc., Essex Pharma, EU Programmes, European society of gastrointestinal and abdominal radiology, Euroscreen S.A., F20 Biotech GmbH, Ferring Pharmaceuticals A/S, Fibrex Medical Inc., Focused Ultrasound Surgery Foundation, Fraunhofer Gesellschaft, GALA Therapeutics, US, Galena Biopharma, Galmed Research and Development Ltd., Ganymed, GBG Forschungs GmbH, GE, Gentech. Inc., Genmab A/S, Genzyme Europe B.V., GETNE (Grupo Espanol de Tumores Neuroendocrinos), Gilead Sciences, Inc., Glaxo Smith Kline, Glycotype GmbH Berlin, Goethe Uni Frankfurt, Guerbet, Guidant Europe NV, Halozyme, Hans-Böckler-Stiftung, Hewlett Packard GmbH, Holaira Inc., Horizon Therapeutics Ireland, ICON (CRO), Idera Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Ignyta, Inc., Immunomedics Inc., Immunocore, Inari Medical Europe GmbH Basel, Incyte, INC Research, Innate Pharma, InSightec Ltd., Inspiremd, InVentiv Health Clinical UK Ltd., Inventivhealth, IO Biotech ApS Copenhagen, IOMEDICO, IONIS, IPSEN Pharma, IQVIA ISA Therapeutics, Isis Pharmaceuticals Inc., ITM Solucin GmbH, Jansen-Cilag GmbH, Kantar Health GmbH (CRO), Kartos Therapeutics, Inc., Karyopharm Therapeutics, Inc., Kendle/MorphoSys AG, Kite Pharma, Kli Fo Berlin Mitte, Kura Oncology, Labcorb, La Roche, Land Berlin, Lilly GmbH, Lion Biotechnology, Lombard Medical, Loxo Oncology, Inc., LSK BioPartners, USA, Lundbeck GmbH, LUX Biosciences, LYSARC, MacroGenics, MagForce, MedImmune Inc., MedImmune Limited, Medpace, Medpace Germany GmbH (CRO), MedPass (CRO), Medtronic, Medtraveo GmbH, Merck, Merrimack Pharmaceuticals Inc., MeVis Medical Solutions AG, Millenium Pharmaceuticals Inc., Miltenyi Biomedicine GmbH, Bergisch Gladbach, miRagen Boukider, Mologen, Monika Kutzner Stiftung, MophoSys AG, MSD Sharp, Nektar Therapeutics, NeoVacs SA, Netzwerkverbund Radiologie, Neurocrine Biosciences Inc., US, Newlink Genetics Corporation, Nexus Oncology, NIH, NOGGO Berlin, Nord-Ostddeutsche Gesellschaft e.V., Novartis, Novocure, Nuvisan, Ockham oncology, Odonate Therapeutics San Diego, OHIRC Kanada, Oppilan Pharma ldt., London, Orion Corporation Orion Pharma, OSE Immunotherapeutics, Parexel CRO Service, Pentixal Pharma GmbH Perceptive, Pfizer GmbH, PharmaCept GmbH, Pharma Mar, Pharmaceutical Reseach Associates GmbH (PRA), Pharmacyclics Inc., Philipps, Philogen s.p.a. Siena, Pliant therapeutics San Francisco, PIQUR Therapeutics Ltd., Pluristem, PneuRX.Inc., Portola Pharmaceuticals, PPD (CRO), PRaint, Precision GmbH, Premier-research, Priovant Therapeutics USA, Provectus Biopharmaceuticals, Inc., psi-cro, Pulmonx International Sarl, Quintiles GmbH, Radiobotics ApS, Regeneraon Pharmaceuticals Inc., Replimune, Respicardia, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Boston USA, Roche, Salix Pharmaceuticals Inc., Samsung, Sanofi, sanofis-aventis S.A., Sarepta Therapeutics, Cambridge, US, Saving Patient’s Lives Medical B.V., Schumacher GmbH, Seagen, Seattle Genetics, Servier (CRO), SGS Life Science Sercives (CRO), Shape Memorial Midical Inc., USA, Shire Human Genetic Therapies, Siemens, Silena Therapeutics, SIRTEX Medical Europe GmbH, SOTIO Biotech, Boston, Spectranetics GmbH, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Stiftung Charite/BIH, St. Jude Medical, Stiftung Wolfgang Schulze, Syneos Health UK, Ltd., Symphogen, Taiho Oncology, Inc., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Target Pharma Solutions Inc., TauRx Therapeutics Ltd., Terumo Medical Corporation, Tesaro, tetec-ag, TEVA, Theorem, Theradex, Theravance, Threshold Pharmaceuticals Inc., TNS Healthcare GmbH, Toshiba, UCB Pharma, Ulrich GmbH Ulm, Uni Jena, Uni München, Uni Tübingen, Vaccibody A.S., VDI/VDE, Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated, Viridian Therapeutics, US, Virtualscopis LLC, Winicker-norimed, Wyeth Pharma, Xcovery Holding Company, and Zukunftsfond Berlin (TSB) outside the submitted work.
Figures





References
-
- Xu S., Liu X., Zhang X., Ji H., Wang R., Cui H., Ma J., Nian Y., Wu Y., Cao X. Prostate zones and tumor morphological parameters on magnetic resonance imaging for predicting the tumor-stage diagnosis of prostate cancer. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2023;29:753–760. doi: 10.4274/dir.2023.232284. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rosenkrantz A.B., Meng X., Ream J.M., Babb J.S., Deng F.M., Rusinek H., Huang W.C., Lepor H., Taneja S.S. Likert score 3 prostate lesions: Association between whole-lesion ADC metrics and pathologic findings at MRI/ultrasound fusion targeted biopsy. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 2016;43:325–332. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24983. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

