Limited Variation in Bacterial Communities of Scaphoideus titanus (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) Across European Populations and Different Life Stages
- PMID: 39590429
- PMCID: PMC11595099
- DOI: 10.3390/insects15110830
Limited Variation in Bacterial Communities of Scaphoideus titanus (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) Across European Populations and Different Life Stages
Abstract
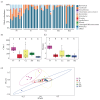
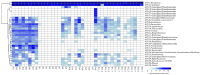
The Nearctic leafhopper Scaphoideus titanus (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) is the primary vector of 'Candidatus Phytoplasma vitis', the causative agent of Flavescence doreé in Europe. Although microorganisms play an important role in the ecology and behavior of insects, knowledge about the interaction between S. titanus and microbes is limited. In this study, we employed an amplicon metabarcoding approach for profiling the V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene to characterize the bacterial communities of S. titanus across several populations from four European localities. Additionally, we investigated changes in bacterial communities between nymphal and adult stages. In total, we identified 7,472 amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) in adults from the European populations. At the genus level, 'Candidatus Karelsulcia' and 'Candidatus Cardinium' were the most abundant genera, with both being present in every individual. While we found significant changes in the microbial composition of S. titanus across different European populations, no significant differences were observed between nymphal and adult stages. Our study reveals new insights into the microbial composition of S. titanus and highlights the role of geography in influencing its bacterial community.
Keywords: 16S rRNA gene metabarcoding; Cardinium; Karelsulcia; Scaphoideus titanus; bacterial communities; endosymbionts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Alma A., Lessio F., Nickel H. Insects as Phytoplasma Vectors: Ecological and Epidemiological Aspects. In: Bertaccini A., Weintraub P.G., Rao G.P., Mori N., editors. Phytoplasmas: Plant Pathogenic Bacteria—II: Transmission and Management of Phytoplasma—Associated Diseases. Springer; Singapore: 2019. pp. 1–25.
-
- Gonella E., Benelli G., Arricau-Bouvery N., Bosco D., Duso C., Dietrich C.H., Galetto L., Rizzoli A., Jović J., Mazzoni V., et al. Scaphoideus titanus Up-to-the-Minute: Biology, Ecology, and Role as a Vector. Entomologia. 2024;44:481–496. doi: 10.1127/entomologia/2023/2597. - DOI
-
- Bonfils J., Schvester D. The Leafhoppers (Homoptera: Auchenorrhyncha) and Their Relationship with Vineyards in South-Western France. Ann. Epiphyt. 1960;11:325–336.
-
- Aguin-Pombo D., Aguiar A.M.F., Cravo D. First Report of Scaphoideus titanus for Madeira Island. EPPO Bull. 2020;50:564–567. doi: 10.1111/epp.12683. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

