Left Atrial Strain: State of the Art and Clinical Implications
- PMID: 39590585
- PMCID: PMC11595645
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm14111093
Left Atrial Strain: State of the Art and Clinical Implications
Abstract
The assessment of left atrial strain (LAS) has emerged as an essential component in the evaluation of cardiac function, especially in pathologies such as heart failure and atrial fibrillation. This narrative review aims to outline the available methods for assessing LAS with a major emphasis on speckle-tracking echocardiography techniques. Other imaging modalities, including cardiac magnetic resonance and cardiac computed tomography, also provide important information on LA dynamics but have disadvantages with respect to cost and availability. The current narrative review underlines basic concepts such as the accurate assessment of LAS and discusses the clinical relevance of LAS by pointing out its significant diagnostic and prognostic role in several cardiovascular conditions. The aim of this article is to discuss the current integration of LAS into clinical practice with a view to further improving patient management and treatment strategies.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; left atrial strain; speckle-tracking echocardiography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
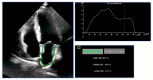
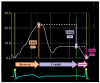
References
-
- Hinojar R., Zamorano J.L., Fernández-Méndez M., Esteban A., Plaza-Martin M., González-Gómez A., Carbonell A., Rincón L.M., Nácher J.J.J., Fernández-Golfín C. Prognostic Value of Left Atrial Function by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Feature Tracking in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging. 2019;35:1055–1065. doi: 10.1007/s10554-019-01534-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

