Free-Standing Carbon Nanofiber Films with Supported Cobalt Phosphide Nanoparticles as Cathodes for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction in a Microbial Electrolysis Cell
- PMID: 39591089
- PMCID: PMC11597106
- DOI: 10.3390/nano14221849
Free-Standing Carbon Nanofiber Films with Supported Cobalt Phosphide Nanoparticles as Cathodes for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction in a Microbial Electrolysis Cell
Abstract
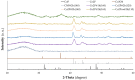
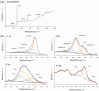
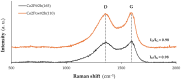
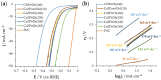
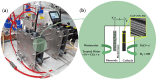
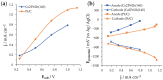
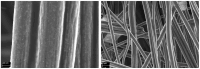
High-performance and cost-efficient electrocatalysts and electrodes are needed to improve the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) for the hydrogen (H2) generation in electrolysers, including microbial electrolysis cells (MECs). In this study, free-standing carbon nanofiber (CNF) films with supported cobalt phosphide nanoparticles have been prepared by means of an up-scalable electrospinning process followed by a thermal treatment under controlled conditions. The produced cobalt phosphide-supported CNF films show to be nanoporous (pore volume up to 0.33 cm3 g-1) with a high surface area (up to 502 m2 g-1) and with a suitable catalyst mass loading (up to 0.49 mg cm-2). Values of overpotential less than 140 mV at 10 mA cm-2 have been reached for the HER in alkaline media (1 M KOH), which demonstrates a high activity. The high electrical conductivity together with the mechanical stability of the free-standing CNF films allowed their direct use as cathodes in a MEC reactor, resulting in an exceptionally low voltage operation (0.75 V) with a current density demand of 5.4 A m-2. This enabled the production of H2 with an energy consumption below 30 kWh kg-1 H2, which is highly efficient.
Keywords: carbon nanofiber (CNF); cathodes; cobalt phosphide; electrocatalyst; electrospinning; free-standing films; hydrogen evolution reaction (HER); microbial electrolysis cells (MECs); nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Yue M., Lambert H., Pahon E., Roche R., Jemei S., Hissel D. Hydrogen Energy Systems: A Critical Review of Technologies, Applications, Trends and Challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021;146:111180. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2021.111180. - DOI
-
- [(accessed on 5 September 2024)]. Available online: https://Commission.Europa.Eu/Strategy-and-Policy/Priorities-2019-2024/Eu....
-
- El-Shafie M. Hydrogen Production by Water Electrolysis Technologies: A Review. Results Eng. 2023;20:101426. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2023.101426. - DOI
-
- Kadier A., Simayi Y., Abdeshahian P., Azman N.F., Chandrasekhar K., Kalil M.S. A Comprehensive Review of Microbial Electrolysis Cells (MEC) Reactor Designs and Configurations for Sustainable Hydrogen Gas Production. Alex. Eng. J. 2016;55:427–443. doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2015.10.008. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

