First-in-Human Phase I Trial to Assess the Safety and Immunogenicity of an Orf Virus-Based COVID-19 Vaccine Booster
- PMID: 39591190
- PMCID: PMC11599021
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12111288
First-in-Human Phase I Trial to Assess the Safety and Immunogenicity of an Orf Virus-Based COVID-19 Vaccine Booster
Abstract
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 has necessitated the development of versatile vaccines capable of addressing evolving variants. Prime-2-CoV_Beta, a novel Orf virus-based COVID-19 vaccine, was developed to express the SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid antigens. This first-in-human, phase I, dose-finding clinical trial was conducted to assess the safety, reactogenicity, and immunogenicity of Prime-2-CoV_Beta as a booster in healthy adults. From June 2022 to June 2023, 60 participants in Germany received varying doses of Prime-2-CoV_Beta. The study demonstrated a favorable safety profile, with no serious adverse events (AEs) reported. All AEs were mild (107) or moderate (10), with the most common symptoms being pain at the injection site, fatigue, and headache. Immunogenicity assessments revealed robust vaccine-induced antigen-specific immune responses. High doses notably elicited significant increases in antibodies against the spike and nucleocapsid proteins as well as neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and its variants. Additionally, the vaccine did not induce ORFV-neutralizing antibodies, indicating the potential for repeated administration. In conclusion, Prime-2-CoV_Beta was safe, well tolerated, and immunogenic, demonstrating potential as a broadly protective vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 and its variants. These promising results support further evaluation of higher doses and additional studies to confirm efficacy and long-term protection. This trial was registered at ClinicalTrials, NCT05389319.
Keywords: COVID-19; Orf virus; Parapoxvirus; SARS-CoV-2; first-in-human; immunogenicity; phase 1; safety; vaccine; viral vector.
Conflict of interest statement
R.A. holds ownership interest in Prime Vector Technologies GmbH, a company involved in the development of ORFV-based vaccines. Additionally, R.A. and A.R. are inventors of patents related to ORFV, including a patent application of Prime-2-CoV_Beta (EP23730776). All other authors declare no competing interest. M.W.L. is an inventor of patents owned by Immatics Biotechnologies unrelated to this present work and has acted as a paid consultant in cancer and immunology for Boehringer Ingelheim.
Figures

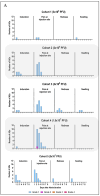

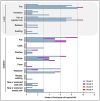


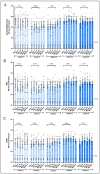


References
-
- World Health Organization 2023 Data.Who.int, WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard > Vaccines [Dashboard] [(accessed on 30 July 2024)]. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/vaccines.
-
- Edouard Mathieu H.R., Rodés-Guirao L., Appel C., Giattino C., Hasell J., Macdonald B., Dattani S., Beltekian D., Ortiz-Ospina E., Roser M. Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19) [(accessed on 30 July 2024)]. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . COVID Data Tracker. Department of Health and Human Services; Atlanta, GA, USA: [(accessed on 29 July 2024)]. Available online: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker.
-
- Cascella M., Rajnik M., Aleem A., Dulebohn S.C., Di Napoli R. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19) StatPearls; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2024. - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

