Therapeutic Potential of Bee and Wasp Venom in Anti-Arthritic Treatment: A Review
- PMID: 39591207
- PMCID: PMC11598298
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins16110452
Therapeutic Potential of Bee and Wasp Venom in Anti-Arthritic Treatment: A Review
Abstract
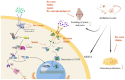
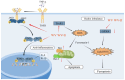
Arthritis has a high global prevalence. During the early ancient human era, bee (Apis) venom therapy was employed in Egypt, Greece, and China to alleviate ailments such as arthritis and neuralgia. In addition, bee venom has long been used as a traditional medicine for immune-related diseases in Korea. Wasp (Vespa) venom is a folk medicine of the Jingpo people in Yunnan, China, and has been widely used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. In spite of this, the underlying mechanisms of bee and wasp venoms for the treatment of arthritis are yet to be fully understood. In recent years, researchers have investigated the potential anti-arthritic properties of bee and wasp venoms. Studies have shown that both bee and wasp venom can improve swelling, pain, and inflammation caused by arthritis. The difference is that bee venom reduces arthritis damage to bone and cartilage by inhibiting the IRAK2/TAK1/NF-κB signaling pathway, NF-κB signaling pathway, and JAK/STAT signaling pathway, as well as decreasing osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting the RANKL/RANK signaling pathway. Wasp venom, on the other hand, regulates synovial cell apoptosis via the Bax/Bcl-2 signaling pathway, inhibits the JAK/STAT signaling pathway to reduce inflammation production, and also ameliorates joint inflammation by regulating redox balance and iron death in synovial cells. This review provides a detailed overview of the various types of arthritis and their current therapeutic approaches; additionally, it comprehensively analyzes the therapeutic properties of bee venom, wasp venom, or venom components used as anti-arthritic drugs and explores their mechanisms of action in anti-arthritic therapy.
Keywords: arthritis; bee venom; component; mechanism; wasp venom.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors affirm that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could be perceived as exerting any influence on the findings presented in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive, and anti-arthritic activities of Indian Apis dorsata bee venom in experimental animals: biochemical, histological, and radiological assessment.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2015 Apr;37(2):171-84. doi: 10.3109/08923973.2015.1009996. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2015. PMID: 25689950
-
The therapeutic effect of wasp venom (Vespa magnifica, Smith) and its effective part on rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes through modulating inflammation, redox homeostasis and ferroptosis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Dec 5;317:116700. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116700. Epub 2023 Jun 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37315652
-
Therapeutic application of anti-arthritis, pain-releasing, and anti-cancer effects of bee venom and its constituent compounds.Pharmacol Ther. 2007 Aug;115(2):246-70. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.04.004. Epub 2007 May 6. Pharmacol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17555825 Review.
-
Pharmacological Alternatives for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders: Wasp and Bee Venoms and Their Components as New Neuroactive Tools.Toxins (Basel). 2015 Aug 18;7(8):3179-209. doi: 10.3390/toxins7083179. Toxins (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26295258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting TNF-α and NF-κB activation by bee venom: role in suppressing adjuvant induced arthritis and methotrexate hepatotoxicity in rats.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 20;8(11):e79284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079284. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24278124 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Harnessing bee venom for inflammatory diseases management: from traditional medicine to nanotechnology.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;398(8):9797-9815. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03991-6. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40072552 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous