Toxigenic Cyanobacteria and Microcystins in a Large Northern Oligotrophic Lake Onego, Russia
- PMID: 39591212
- PMCID: PMC11598714
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins16110457
Toxigenic Cyanobacteria and Microcystins in a Large Northern Oligotrophic Lake Onego, Russia
Abstract
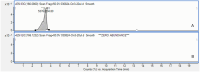
Toxigenic cyanobacteria and microcystins in the oligotrophic pelagic zone and mesotrophic bay of Lake Onego-the second largest lake in Europe-were found for the first time. Microscopic analysis revealed that Dolichospermum lemmermannii, D. circinale and D. spiroides dominated in bloom spots in the oligotrophic zone of the lake and D. flos-aquae and Microcystis aeruginosa OKin the eutrophic bay. The abundance of cyanobacteria in bloom spots is potentially hazardous for humans and animals. PCR-analysis showed that mcyA gene involved in microcystin biosynthesis was found in cyanobacteria of the genera Dolichospermum and Microcystis. Five structural variants of intracellular microcystins were detected in a trace amount using high-performance liquid chromatography-mass-spectrometry of high resolution. The most hazardous hepatotoxin, MC-LR, was found only in the eutrophic bay. In the present study, the reasons for the low cyanotoxin content in the phytoplankton dominated by Dolichospermum are discussed. The findings of our study make a significant contribution to the accumulation of facts which state that toxigenic cyanobacterial blooms can occur in large oligotrophic lakes.
Keywords: Lake Onego; cyanobacteria; microcystins; toxigenic species; water bloom.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
First observation of microcystin- and anatoxin-a-producing cyanobacteria in the easternmost part of the Gulf of Finland (the Baltic Sea).Toxicon. 2019 Jan;157:18-24. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2018.11.005. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Toxicon. 2019. PMID: 30448287
-
High diversity of microcystins in a Microcystis bloom from an Algerian lake.Environ Pollut. 2016 Sep;216:836-844. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.06.055. Epub 2016 Jul 6. Environ Pollut. 2016. PMID: 27394081
-
World's largest oligotrophic Lake Baikal: Concerns about cyanobacterial blooms and potential microcystin producers along the littoral zone.Harmful Algae. 2025 Apr;144:102841. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2025.102841. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Harmful Algae. 2025. PMID: 40187794
-
Using Microcystin Gene Copies to Determine Potentially-Toxic Blooms, Example from a Shallow Eutrophic Lake Peipsi.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Mar 26;12(4):211. doi: 10.3390/toxins12040211. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32225013 Free PMC article.
-
Community Structure and Toxicity Potential of Cyanobacteria during Summer and Winter in a Temperate-Zone Lake Susceptible to Phytoplankton Blooms.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Aug 14;16(8):357. doi: 10.3390/toxins16080357. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39195767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chorus I. Cyanotoxins: Occurrence, Causes, Consequences. Springer; Berlin, Germany: 2001. - DOI
-
- O’Neil J.M., Davis T.W., Burford M.A., Gobler C.J. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae. 2012;14:313–334. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2011.10.027. - DOI
-
- Sukharevich V.I., Polak Y.M. Global occurrence of cyanobacteria: Causes and effects (review) Inland Water Biol. 2020;4:566–575. doi: 10.1134/S1995082920060140. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

