Multicentennial cycles in continental demography synchronous with solar activity and climate stability
- PMID: 39592580
- PMCID: PMC11599897
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54474-w
Multicentennial cycles in continental demography synchronous with solar activity and climate stability
Abstract
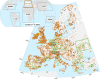
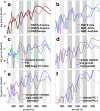
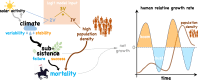
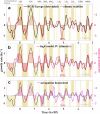
Human population dynamics and their drivers are not well understood, especially over the long term and on large scales. Here, we estimate demographic growth trajectories from 9 to 3 ka BP across the entire globe by employing summed probability distributions of radiocarbon dates. Our reconstruction reveals multicentennial growth cycles on all six inhabited continents, which exhibited matching dominant frequencies and phase relations. These growth oscillations were often also synchronised with multicentennial variations in solar activity. The growth cycle for Europe, reconstructed based on >91,000 radiocarbon dates, was backed by archaeology-derived settlement data and showed only a weak correlation with mean climate states, but a strong correlation with the stability of these states. We therefore suggest a link between multicentennial variations in solar activity and climate stability. This stability provided more favourable conditions for human subsistence success, and seems to have induced synchrony between regional growth cycles worldwide.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ricklefs, R. E.The Economy of Nature (Macmillan, 2008).
-
- Dong, J., Li, W., Cao, Y. & Fang, J. How does technology and population progress relate? An empirical study of the last 10,000 years. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change103, 57–70 (2016).
-
- Palmisano, A., Lawrence, D., de Gruchy, M. W., Bevan, A. & Shennan, S. Holocene regional population dynamics and climatic trends in the Near East: A first comparison using archaeo-demographic proxies. Quatern. Sci. Rev.252, 106739 (2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

