Predictive dermoscopic features of cryotherapy treatment response in cutaneous warts
- PMID: 39592755
- PMCID: PMC11599726
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-80608-7
Predictive dermoscopic features of cryotherapy treatment response in cutaneous warts
Abstract
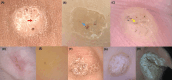
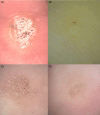
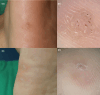
The utility of dermoscopy for the diagnosis of cutaneous warts is well known. However, its role in predicting the outcome of cryotherapy for cutaneous warts remains unexplored. To identify dermoscopic features predicting treatment responses in cryotherapy for cutaneous warts. We conducted a retrospective analysis of 119 warts in 103 patients. Responses were categorized as complete, partial, or none after three sessions of cryotherapy within 4 months. The evaluated features included vascularity, papillary patterns, and margin characteristics. Marked surface scales and well-defined margins were common in complete responses. Minimal surface scales and smooth patterns were observed in less responsive cases. In the group with a complete response, marked surface scales were observed 6.59 times more frequently, well-defined margins were 4.1 times more common, and dots were 4.07 times more common compared to the group with no response. Common warts responded well when showing vascularity and marked surface scales, whereas plantar warts responded positively when showing background erythema. Dermoscopic features, such as dots, marked surface scales, and well-defined margins, predict a favorable cryotherapy response in cutaneous warts. Plantar warts respond positively in the presence of perilesional erythema, whereas common warts exhibit vascularity and marked surface scales for a better response to cryotherapy.
Keywords: Cryotherapy; Dermoscopy; Human papilloma virus; Predictive factors; Viral infection; Warts.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Informed consent: The study was a retrospective study that received IRB approval. At that time, the IRB determined that not only did it meet the following two requirements, but it was also included in the exemption from consent because sensitive information was not included in the study. Requirement 1: Obtaining consent from the research subjects is practically impossible during the course of the study or it is determined that it would seriously affect the validity of the research. Requirement 2: There is no reason to presume that the research subjects would refuse consent, and the exemption from consent poses extremely low risk to the research subjects. Institutional review board statement: Approved by the Institutional Review Board of Pusan National University Hospital Clinical Trial Center (IRB No.: H-2401–010-135).
Figures
References
-
- Khozeimeh, F. et al. An expert system for selecting wart treatment method. Comput. Biol. Med.81, 167–175. 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2016.12.020 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Ghiasi, M. M. & Zendehboudi, S. Decision tree-based methodology to select a proper approach for wart treatment. Comput. Biol. Med.108, 400–409. 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.05.002 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

