Enhancing the solubility and antibacterial activity of novel molecular salts of enrofloxacin drug with isomeric pyridinedicarboxylic acids
- PMID: 39592802
- PMCID: PMC11599901
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-80665-y
Enhancing the solubility and antibacterial activity of novel molecular salts of enrofloxacin drug with isomeric pyridinedicarboxylic acids
Abstract
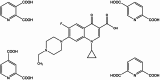
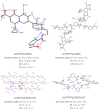
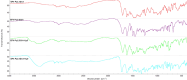
Enrofloxacin (EFX) is a third-generation synthetic fluoroquinolone with a broad spectrum of antibacterial activity but suffers from low water solubility, affecting its bioavailability. This study attempts to enhance the physicochemical and biological properties of enrofloxacin by converting it into multicomponent forms using crystal engineering concepts. Cocrystallization of enrofloxacin with isomeric pyridine-2,n-dicarboxylic acids (n = 3,4,5,6) resulted in four new crystalline salts (1:1): EFX·Py2,3DCA, EFX·Py2,4DCA, EFX·Py2,5DCA·H2O and EFX·Py2,6DCA·H2O; two of these are monohydrates. The protonation of the nitrogen atom of the piperazine moiety and the presence of crystallization water molecules were confirmed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Thermogravimetric analysis provided information on the thermal behaviour of multicomponent forms. The biological studies showed that the obtained salts are characterized by high antibacterial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, and their haemolytic activity is low. The new salts demonstrate significantly greater solubility in water compared to the parent drug, along with enhanced antibacterial activity; hence, pyridinedicarboxylic acids appear to be efficient cocrystallizing agents for improving the efficacy of pharmaceutical ingredients.
Keywords: Antibacterial activity; Crystal engineering; Crystal structure; Enrofloxacin; Fluoroquinolones; Solubility.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Emmerson, A. M. & Jones, A. M. The quinolones: Decades of development and use. J. Antimicrob. Chemother.51(Suppl. 1), 13–20. 10.1093/jac/dkg208 (2003). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

