The ZJU index is associated with the risk of sarcopenia in American adults aged 20-59: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 39593075
- PMCID: PMC11590360
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-024-02373-w
The ZJU index is associated with the risk of sarcopenia in American adults aged 20-59: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: The ZJU index is an innovative computational method which integrates BMI, FBG, TG, and ALT to AST ratio. It strongly correlates with measures of lipid metabolism and glucose intolerance. No researches have yet explored the relationship between the ZJU index and sarcopenia.
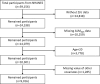
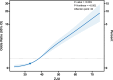
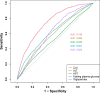
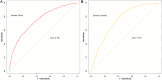
Methods: We analyzed NHANES data from 2011 to 2018, dividing the ZJU index into quartiles. The association was investigated by adjusting for confounders using multivariable linear and logistic regression analysis. Results were visualized through RCS regression and threshold effect analyses. We conducted various subgroup and sensitivity analyses and plotted ROC curves to assess prediction efficacy, with the AUC as the measure of accuracy.
Results: As the ZJU index increases, the prevalence of sarcopenia also rises. Following the control of potential confounders via logistic regression analysis, our research identified a distinct relationship between the ZJU index and sarcopenia, which was statistically significant (P < 0.001), with higher ZJU index values associated with increased risk (OR = 12.40, 95% CI: 8.46-18.17). Interaction analysis suggests that the relationship between the ZJU index and the risk of developing sarcopenia varies significantly between males and females across different ZJU index levels. ROC analysis for the ZJU index shows an AUC of 0.749.
Conclusions: The ZJU index significantly correlates with a heightened risk of sarcopenia in Americans, suggesting its potential as a predictive marker for sarcopenia.
Keywords: Appendicular lean mass; Cross-sectional study; NHANES; Sarcopenia; ZJU index.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Institutional review board: The study followed the ethical guidelines outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the National Center for Health Statistics Institutional Review Board. Informed consent: All participants provided informed consent before enrollment. Conflict of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

