YTHDF2 promotes anaplastic thyroid cancer progression by activating the DDIT4/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- PMID: 39593172
- PMCID: PMC11600618
- DOI: 10.1186/s13062-024-00566-y
YTHDF2 promotes anaplastic thyroid cancer progression by activating the DDIT4/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: RNA methylation, an important reversible post-transcriptional modification in eukaryotes, has emerged as a prevalent epigenetic alteration. However, the role of the m6A reader YTH domain family 2 (YTHDF2) has not been reported in anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC) and its biological mechanism is unclear.
Methods: The relationship between YTHDF2 expression and ATC was determined using data sets and tissue samples. A range of analytical techniques were employed to investigate the regulatory mechanism of YTHDF2 in ATC, including bioinformatics analysis, m6A dot-blot analysis, methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeRIP-seq), RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays, RNA sequencing, RNA stability assays and dual luciferase reporter gene assays. In vitro and in vivo assays were also conducted to determine the contribution of YTHDF2 to ATC development.
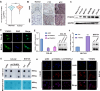
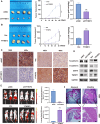
Results: YTHDF2 expression was significantly increased in ATC. The comprehensive in vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrated that YTHDF2 knockdown significantly attenuated ATC proliferation, invasion, migration, and apoptosis promotion, whereas YTHDF2 overexpression yielded the opposite trend. Mechanistically, RNA-seq, MeRIP-seq and RIP-seq analysis, and molecular biology experiments demonstrated that YTHDF2 accelerated the degradation of DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 or regulated in DNA damage and development 1 (DDIT4, or REDD1) mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner, which in turn activated the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and induced activation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), thereby promoting ATC tumor progression.
Conclusions: This study is the first to demonstrate that elevated YTHDF2 expression levels suppress DDIT4 expression in an m6A-dependent manner and activate the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, thereby promoting ATC progression. YTHDF2 plays a pivotal role in ATC progression, and it may serve as a promising therapeutic target in the future.
Keywords: AKT; Anaplastic thyroid cancer; YTHDF2; m6A; mTOR.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Ethical Review Committee of the Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital and was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (Project No. KY2023-306). All animals were housed and handled according to the guidelines of the Ethical Review Committee of Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (acceptance No. S2023-357-02.20160006). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2024, 74(3):229-263. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 2023A1515010175/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- No. 2020A1515010126/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2024A04J4974/Guangzhou Science and Technology Scheme
- a9Z04JKM2022E036a0/Young and Middle-Aged Thyroid Physician Research Program
- No.KJ012019441/Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital Scientific Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of Guangdong Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

