Unlocking the Potentials of Large Language Models in Orthodontics: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 39593805
- PMCID: PMC11591942
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering11111145
Unlocking the Potentials of Large Language Models in Orthodontics: A Scoping Review
Abstract
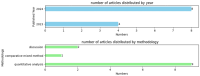
(1) Background: In recent years, large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT have gained significant attention in various fields, including dentistry. This scoping review aims to examine the current applications and explore potential uses of LLMs in the orthodontic domain, shedding light on how they might improve dental healthcare. (2) Methods: We carried out a comprehensive search in five electronic databases, namely PubMed, Scopus, Embase, ProQuest and Web of Science. Two authors independently screened articles and performed data extraction according to the eligibility criteria, following the PRISMA-ScR guideline. The main findings from the included articles were synthesized and analyzed in a narrative way. (3) Results: A total of 706 articles were searched, and 12 papers were eventually included. The applications of LLMs include improving diagnostic and treatment efficiency in orthodontics as well as enhancing communication with patients. (4) Conclusions: There is emerging research in countries worldwide on the use of LLMs in orthodontics, suggesting an upward trend in their acceptance within this field. However, the potential application of LLMs remains in its early stage, with a noticeable lack of extensive studies and tailored products to address specific clinical needs.
Keywords: ChatGPT; Chatbot; GPT; LLMs; artificial intelligence; generative AI; large language models; orthodontics; scoping review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Large Language Models in Transforming Emergency Medicine: Scoping Review.JMIR Med Inform. 2024 May 10;12:e53787. doi: 10.2196/53787. JMIR Med Inform. 2024. PMID: 38728687 Free PMC article.
-
Large language models for conducting systematic reviews: on the rise, but not yet ready for use-a scoping review.J Clin Epidemiol. 2025 May;181:111746. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2025.111746. Epub 2025 Feb 26. J Clin Epidemiol. 2025. PMID: 40021099
-
A Systematic Review of ChatGPT and Other Conversational Large Language Models in Healthcare.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 27:2024.04.26.24306390. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.26.24306390. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Med Internet Res. 2024 Nov 7;26:e22769. doi: 10.2196/22769. PMID: 38712148 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Applications of large language models in psychiatry: a systematic review.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Jun 24;15:1422807. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1422807. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38979501 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence-based potential of generative artificial intelligence large language models in orthodontics: a comparative study of ChatGPT, Google Bard, and Microsoft Bing.Eur J Orthod. 2024 Apr 13:cjae017. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjae017. Online ahead of print. Eur J Orthod. 2024. PMID: 38613510
Cited by
-
Assessing and enhancing the reliability of Chinese large language models in dental implantology.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Jul 26;25(1):1242. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-06648-1. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40713564 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the accuracy of generative artificial intelligence models in dental age estimation based on the Demirjian's method.Front Dent Med. 2025 Jul 29;6:1634006. doi: 10.3389/fdmed.2025.1634006. eCollection 2025. Front Dent Med. 2025. PMID: 40800006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Negnevitsky M. Artificial Intelligence: A Guide to Intelligent Systems. Pearson education; London, UK: 2005.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources