An Integrative Framework for Healthcare Recommendation Systems: Leveraging the Linear Discriminant Wolf-Convolutional Neural Network (LDW-CNN) Model
- PMID: 39594176
- PMCID: PMC11592656
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14222511
An Integrative Framework for Healthcare Recommendation Systems: Leveraging the Linear Discriminant Wolf-Convolutional Neural Network (LDW-CNN) Model
Abstract
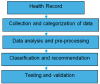
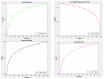
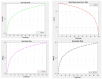
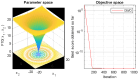
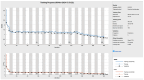
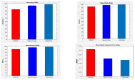
In the evolving healthcare landscape, recommender systems have gained significant importance due to their role in predicting and anticipating a wide range of health-related data for both patients and healthcare professionals. These systems are crucial for delivering precise information while adhering to high standards of quality, reliability, and authentication. Objectives: The primary objective of this research is to address the challenge of class imbalance in healthcare recommendation systems. This is achieved by improving the prediction and diagnostic capabilities of these systems through a novel approach that integrates linear discriminant wolf (LDW) with convolutional neural networks (CNNs), forming the LDW-CNN model. Methods: The LDW-CNN model incorporates the grey wolf optimizer with linear discriminant analysis to enhance prediction accuracy. The model's performance is evaluated using multi-disease datasets, covering heart, liver, and kidney diseases. Established error metrics are used to compare the effectiveness of the LDW-CNN model against conventional methods, such as CNNs and multi-level support vector machines (MSVMs). Results: The proposed LDW-CNN system demonstrates remarkable accuracy, achieving a rate of 98.1%, which surpasses existing deep learning approaches. In addition, the model improves specificity to 99.18% and sensitivity to 99.008%, outperforming traditional CNN and MSVM techniques in terms of predictive performance. Conclusions: The LDW-CNN model emerges as a robust solution for multidisciplinary disease prediction and recommendation, offering superior performance in healthcare recommender systems. Its high accuracy, alongside its improved specificity and sensitivity, positions it as a valuable tool for enhancing prediction and diagnosis across multiple disease domains.
Keywords: deep learning; grey wolf optimization; health records; healthcare; linear discriminant analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ricci F., Rokach L., Shapira B. Introduction to Recommender Systems Handbook. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2011. pp. 1–35.
-
- Sánchez-Moreno D., López Batista V.F., Muñoz Vicente M.D., Sánchez Lázaro Á.L., Moreno-García M.N. Social Network Community Detection to Deal with Gray-Sheep and Cold-Start Problems in Music Recommender Systems. Information. 2024;15:138. doi: 10.3390/info15030138. - DOI
-
- Javaid M., Haleem A., Singh R.P., Ahmed M. Computer vision to enhance healthcare domain: An overview of features, implementation, and opportunities. Intell. Pharm. 2024. in press . - DOI
-
- Al-Assaf K., Alzahmi W., Alshaikh R., Bahroun Z., Ahmed V. The Relative Importance of Key Factors for Integrating Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems and Performance Management Practices in the UAE Healthcare Sector. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2024;8:122. doi: 10.3390/bdcc8090122. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

