Enhancing Proton Therapy Efficacy Through Nanoparticle-Mediated Radiosensitization
- PMID: 39594590
- PMCID: PMC11593106
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13221841
Enhancing Proton Therapy Efficacy Through Nanoparticle-Mediated Radiosensitization
Abstract
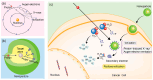
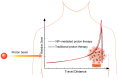
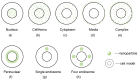
Proton therapy, characterized by its unique Bragg peak, offers the potential to optimize the destruction of cancer cells while sparing healthy tissues, positioning it as one of the most advanced cancer treatment modalities currently available. However, in comparison to heavy ions, protons exhibit a relatively lower relative biological effectiveness (RBE), which limits the efficacy of proton therapy. The incorporation of nanoparticles for radiosensitization presents a novel approach to enhance the RBE of protons. This review provides a comprehensive discussion of the recent advancements in augmenting the biological effects of proton therapy through the use of nanoparticles. It examines the various types of nanoparticles that have been the focus of extensive research, elucidates their mechanisms of radiation sensitization, and evaluates the factors influencing the efficiency of this sensitization process. Furthermore, this review discusses the latest synergistic therapeutic strategies that integrate nanoparticle-mediated radiosensitization and outlines prospective directions for the future application of nanoparticles in conjunction with proton therapy.
Keywords: RBE; cancer cells; nanoparticle radiosensitization; proton therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

